White wagtail
"Pied Wagtail" redirects here. For the related African bird, see African Pied Wagtail.
| White Wagtail | |
|---|---|

| |
| M. alba alba | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | M. alba
|
| Binomial name | |
| Motacilla alba Linnaeus, 1758
| |
The White Wagtail (Motacilla alba) is a small passerine bird in the wagtail family Motacillidae, which also includes the pipits and longclaws. This species breeds in much of Europe and Asia and parts of north Africa. It is resident in the mildest parts of its range, but otherwise migrates to Africa. It has a toehold in Alaska as a scarce breeder. In some areas, notably Britain and Ireland, the sub-species Pied Wagtail (M. a. yarrellii) predominates.
This is an insectivorous bird of open country, often near habitation and water. It prefers bare areas for feeding, where it can see and pursue its prey. In urban areas it has adapted to foraging on paved areas such as car parks. It nests in crevices in stone walls and similar natural and man-made structures.
The White Wagtail is the national bird of Latvia.
Taxonomy and systematics
The White Wagtail was one of the many species originally described by Linnaeus in his 18th century work, Systema Naturae, and it still bears its original name of Motacilla alba.[2] The Latin genus name originally meant "little mover", but certain medieval writers thought it meant "wag-tail", giving rise to a new Latin word cilla for "tail".[3] The specific epithet alba is Latin for "white".
Within the wagtail genus Motacilla, the White Wagtail's closest relatives appear to be other black-and-white wagtails such as the Japanese Wagtail, Motacilla grandis, and the White-browed Wagtail, Motacilla madaraspatensis, (and possibly the Mekong Wagtail, Motacilla samveasnae, the phylogenetic position of which is mysterious) with which it appears to form a superspecies. However mtDNA cytochrome b and NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 sequence data suggests that the White Wagtail is itself polyphyletic or paraphyletic (i.e. the species is not itself a single coherent grouping).[4] Other phylogenetic studies using mtDNA however suggest that there is considerable gene flow within the races and the resulting closeness makes Motacilla alba a single species.[5] Some studies have suggested the existence of only two groups : the alboides group, with M. a. alboides, M. a. leucopsis and M. a. personata; and the alba group, with M. a. alba, M. a. yarrellii, M. a. baicalensis, M. a. ocularis, M. a. lugens, and M. a. subpersonata.[6]
Willy Wagtail was a colloquial name used in the Isle of Man, replacing the older name ushag vreck,[7] as well as a common name used in Northern Ireland.[8]
Description
This is a slender bird, 16.5–19 cm (6½–7½ in) in length (East Asian subspecies are longer, to 21 cm (8¼ in), with the characteristic long, constantly wagging tail of its genus. The nominate subspecies Motacilla alba alba is basically grey above and white below, with a white face, black cap and black throat.
There are a number of other subspecies, some of which may have arisen because of partial geographical isolation, such as the resident British form, the Pied Wagtail M. a. yarrellii, which now also breeds in adjacent areas of the neighbouring European mainland. Pied Wagtail, named for naturalist William Yarrell, exchanges the grey colour of the nominate form with black (or very dark grey in females), but is otherwise identical in its behaviour. Other subspecies, the validity of some of which is questionable, differ in the colour of the wings, back, and head, or other features. Some races show sexual dimorphism during the breeding season. As many as six subspecies may be present in the wintering ground in India or Southeast Asia and here they can be difficult to distinguish.[9][10][11][12] Phylogenetic studies using mtDNA suggest that some morphological features have evolved more than once including the back and chin colour. Breeding M. a. yarrellii look much like the nominate race except for the black back, and M. a. alboides of the Himalayas differs from the Central Asian M. a. personata only by its black back. M. a. personata has been recorded breeding in the Siddar Valley of Kashmir of the Western Himalayas.[13] It has also been noted that both back and chin change colour during the pre-basic moult; all black-throated subspecies develop white chins and throats in winter and some black-backed birds are grey-backed in winter.[5][9]
The call of the White Wagtail is a sharp chisick, slightly softer than the version given by Pied Wagtail. The song is a pleasant twittering, more regular in White than Pied, but with little territorial significance, since the male uses a series of contact calls to attract the female.[14]
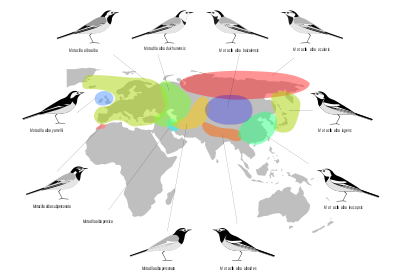
Subspecies
Nine or eleven subspecies are currently recognised. Information on the plumage differences and distribution of the subspecies of White Wagtail is shown below.[15]
| Subspecies | Range | Notes | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. a. alba | Europe from the Iberian Peninsula to Ural Mountains, Turkey, the Levant, Iceland, the Faroe Islands and Greenland's east coast. Some migrate to the south of Europe and Africa down as far as Kenya and Malawi | Nominate subspecies | 
|
| M. a. yarrellii | Great Britain and Ireland, birds in the northern part of the range winter in Spain and North Africa, those further south are resident.[16] | Pied Wagtail. Has a much blacker back than the nominate race, black of throat continues on side of neck | 
|
| M. a. dukhunensis | West Siberian Plain - east Caspian Sea (part of Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan), winters in the Middle East and India. Sometimes included in alba.[16] | Indian Pied Wagtail. The upperparts of this subspecies are paler and more blue-grey than nominate, and has it has a continuous unbroken white panel on wing coverts. | |
| M. a. persica | North central and western Iran. | Intermediate between M. a. dukhunensis and M. a. personata. Often included in alba; appears to be hybrid or intergrade population.[16] | 
|
| M. a. subpersonata | Non-migratory resident of Morocco | Moroccan Wagtail. It has more black on the head than the nominate, and resembles a grey-backed, white-throated African Pied Wagtail[16] | |
| M. a. personata | Hindu Kush, Tian Shan, Altay Mountains (northern Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang) | Masked Wagtail. All-black head with a white face mask | 
|
| M. a. alboides | Himalayas and surrounding area | This subspecies has a black back and a lot of black around the head, a white wing panel and white edges on the secondaries and tertials. | |
| M. a. baicalensis | Russia in Lake Baikal area, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia | Resembles M. a. leucopsis but grey back and less white on head and wing. | |
| M. a. ocularis | Siberia, Far Eastern (Russia, eastwards from Central Siberian Plateau) expanding into West Alaska | ||
| M. a. lugens | Russia Far East (Primorsky Krai, Khabarovsk Krai), Kamchatka Peninsula, Kuril Islands, Sakhalin, Japan (Hokkaidō, Honshū) | Black-backed Wagtail or Kamchatka/Japanese Pied Wagtail, similar to M. a. yarrellii, but has a black eyestripe and white remiges; might have a claim to constitute a distinct species. | 
|
| M. a. leucopsis | China, Korean Peninsula, Taiwan, Japan (Ryukyu Islands, Kyūshū)
expanding into Japan (Honshū), Southeast Asia, India and Oceania |
Amur Wagtail[17][18][19] | 
|
Distribution and habitat

This species breeds throughout Eurasia up to latitudes 75°N, only being absent in the Arctic from areas where the July isotherm is less than 4 °C. It also breeds in the mountains of Morocco and western Alaska. It occupies a wide range of habitats, but is absent from deserts.[14]
White Wagtail is resident in the milder parts of its range such as western Europe and the Mediterranean, but migratory in much of the rest of its range. Northern European breeders winter around the Mediterranean and in tropical and subtropical Africa,[20] and Asiatic birds move to the Middle East, India,[16] and SouthEast Asia.[21] Birds from the North American population also winter in tropical Asia.[22]
Status
This species has a large range, with an estimated gextent of more than 10 million km² (3.8 sq mi). The population size is unknown, but it is believed to be large, as the species is described as "common" in at least parts of its range. Population trends have not been quantified, but the species is not believed to approach the thresholds for the population decline criterion of the IUCN Red List (i.e. declining more than 30% in ten years or three generations). For these reasons, the species is evaluated as Least Concern.[1] The population in Europe appears to be stable.[20] The species has adapted well to human changes to the environment, and has in fact exploited human changes such as man-made structures which are used for nesting sites and increased open areas which are used for foraging.[16]
Behaviour
The most conspicuous habit of this species is a near-constant tail wagging, a trait that has given the species, and indeed the genus, its common name. In spite of the ubiquity of this behaviour, the reasons for it are poorly understood. It has been suggested that it may flush prey, or signal submissiveness to other wagtails. A recent study has suggested instead that it is a signal of vigilance to potential predators.[23]
Diet and feeding
The exact composition of the diet of White Wagtails varies by location, but terrestrial and aquatic insects and other small invertebrates form the major part of the diet. These range from beetles, dragonflies, small snails, spiders, worms, crustaceans, to maggots found in carcasses and, most importantly, flies in the order Diptera.[16] Small fish fry have also been recorded in the diet. The White Wagtail is somewhat unusual in the parts of it range where it is non-migratory as it is an insectivorous bird that continues to feed on insects during the winter (most other insectivorous birds in temperate climates migrate or switch to more vegetable matter).[24]
Breeding
White Wagtails are monogamous and defend breeding territories.[16] The breeding season for most is from April to August, with the season starting later further north. Both sexes are responsible for building the nest, with the male responsible for initiating the nest building and the female for finishing the process. For second broods in the subspecies personata the female alone builds the nest as the male is still provisioning the young.[25] which is a rough cup assembled from twigs, grass, leaves and other plant matter. It is lined with soft materials, including animal hair. The nest is set into a crevice or hole; traditionally in a bank next to a river or ditch, but the species has also adapted to nesting in walls, bridges and buildings. One nest was found in the skull of a walrus. They species will nest in association with other animals, particularly where available the dams of beavers and also inside the nests of Golden Eagles.[25] Around 3-8 eggs are laid, with the usual number being 4-6. Its eggs are cream-coloured, often with a faint bluish-green or turquoise tint, and heavily spotted with reddish brown; they measure, on average, 21 x 15 mm (0.83 x 0.59 inches).[26] Both parents incubate the eggs, although the female generally does so for longer and incubates at night. The eggs begin to hatch after 12 days (sometimes as late as 16 days). Both parents feed the chicks until they fledge at around 14 days, and the chicks are fed for another week after fledging.
Though it is known to be a host species for the Common Cuckoo, the White Wagtail typically deserts its nest if it has been parasitised. Scientists theorise that this occurs because the wagtail is too small to push the intruding egg out of the nest, and too short-billed to destroy the egg by puncturing it.[27]
Various views and plumages
-
Non-breeding- leucopsis race at Jayanti in Buxa Tiger Reserve in Jalpaiguri district of West Bengal, India.
-
White Wagtail (M. a. alba)
-
Pied Wagtail (M. a. yarrellii)
-
Young bird
-
Hybrid between yarrelii and alba, or a yarrelli female
-
Motacilla alba yarrellii, Pied Wagtail in SE England.
-
Non-breeding M. a. leucopsis in India.
-
Male non-breeding M. a. personata race India
References
- ^ a b Template:IUCN2007
- ^ Template:La icon Linnaeus, C (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata. Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). p. 185.
M. pectore nigro, recticibus duabus lateralibus dimidiato oblique albis.
- ^ Jobling, James (1991). A Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198546343.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Voelker, Gary (2002). "Systematics and historical biogeography of wagtails: Dispersal versus vicariance revisited". Condor. 104 (4): 725–739. doi:10.1650/0010-5422(2002)104[0725:SAHBOW]2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}:|format=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help); External link in|format= - ^ a b Pavlova, A., Zink, R. M., Rohwer, S., Koblik, E. A., Red’kin, Y. A., Fadeev, I. V. and
Nesterov, E. V. (2005). "Mitochondrial DNA and plumage evolution in the white wagtail Motacilla alba". J. Avian Biol. 36: 322–336. doi:10.1111/j.0908-8857.2005.03373.x.
{{cite journal}}: line feed character in|author=at position 87 (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Odeen, A. and Alstrom, P. 2001. Evolution of secondary traits in wagtails (genus Motacilla ). In: Odeen A. Effects of post-glacial range expansion and population bottlenecks on species richness. PhD. thesis, Uppsala University.
- ^ Moore AW, Morrison S, Goodwin E (1924). A Vocabulary of the Anglo-Manx Dialect. London: Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ McAfee CI (1996). A Concise Ulster Dictionary. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198631324.
- ^ a b Alstrom, P. & Mild, K. (2003). Pipits and wagtails. Princeton Univ. Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Akhtar,Syed Asad; Prakash,Vibhu (1989). "Streakeyed Pied Wagtail, Motacilla alba ocularis Swinhoe from Harike Lake, Punjab". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 86 (2): 246.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ticehurst,CB (1922). "Notes on Indian wagtails". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 28 (4): 1082–1090.
- ^ Pittie,Aasheesh; Kulkarni,MS; Mathew,Rajeev (1998). "Range extension of White Wagtail Motacilla alba leucopsis at Pocharam Lake, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 95 (2): 347–348.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fenton,LL (1910). "Breeding of the Masked Wagtail (Motacilla personata) in Kashmir". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 19 (4): 992.
- ^ a b Simms, Eric (Author) (1992). Larks, Pipits and Wagtails (Collins New Naturalist). Harper Collins. pp. 233–252. ISBN 000219871.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help); Check|isbn=value: length (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Template:Ja icon Nakamura, Kazue (1985). "Historical change of the geographical distribution of two closely related species of the genus Motacilla in the Japanese Archipelago: a preliminary note". Bulletin of the Kanagawa prefecture Museum of Natural Science. No.16.
{{cite journal}}:|volume=has extra text (help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b c d e f g h Tyler, S. (2004) "Family Motacillidae (Pipits and Wagtails)" pp.777-778 in del Hoyo, J.; Elliot, A. & Christie D. (editors). (2004). Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 9: Cotingas to Pipits and Wagtails. Lynx Edicions. ISBN 84-87334-69-5
- ^ British Ornithologists’ Union Records Committee (22 July 2009). "Changes to Category A of the British List". BOU News. British Ornithologists’ Union. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) [dead link] - ^ Addinall, Stephen (2010). "'Amur Wagtail' in County Durham: new to Britain and the Western Palearctic". British Birds. 103: 260–267.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Rowlands, Adam (2010). "Proposed criteria for BBRC assessment of claims of 'Amur Wagtail'". British Birds. 103: 268–275.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b Snow, David (1998). The Birds of the Western Palearctic concise edition (2 volumes). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 1103–1106. ISBN 0-19-854099-X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Arlott, Norman) (2007). Birds of the Palearctic: Passerines (Collins Field Guide). Harper Collins. pp. 30–31. ISBN 0007147058.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Sibley, David (2000). The North American Bird Guide. Pica Press. ISBN 1-873403-78-4.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: checksum (help) - ^ Randler, C (2006). "Is tail wagging in white wagtails, Motacilla alba, an honest signal of vigilance?" Animal Behaviour 71 (5): 1089-1093 Abstract
- ^ Davies, N.B. (1976). "Food, Flocking and Territorial Behaviour of the Pied Wagtail (Motacilla alba yarrellii Gould) in Winter". The Journal of Animal Ecology. 45 (1). Journal of Animal Ecology, Vol. 45, No. 1: 235–253. doi:10.2307/3777.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b Badyaev, A. V. (1996). "White Wagtail (Moticilla alba')". The Birds of North America Online. Ithaca: Cornell Lab of Ornithology. doi:10.2173/bna.236. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Peyton, Leonard J. (1963). "Nesting and occurrence of White Wagtail in Alaska" (PDF). Condor. 65 (3). The Condor, Vol. 65, No. 3: 232–235. doi:10.2307/1365667. JSTOR 1365667.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Moksnes, Arne (1991). "Rejection Behavior by Common Cuckoo Hosts Towards Artificial Brood Parasite Eggs" (PDF). Auk. 108 (2): 248–254.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
External links
- Wagtail videos, photos & sounds on the Internet Bird Collection
- Norwegian Cyberbirding: Masked, Pied & White Wagtails photos. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- Romani Rise: Pied Wagtail - the Gipsy Bird Pied Wagtails in Welsh Romani culture. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- identification article with pictures (pdf)
- Ageing and sexing (PDF) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta























