Evidence of common descent
| Part of a series on |
| Evolutionary biology |
|---|
 |
Evidence of common descent of living organisms has been discovered by scientists researching in a variety of disciplines over many decades, demonstrating that all life on Earth comes from a single ancestor. This forms an important part of the evidence on which evolutionary theory rests, demonstrates that evolution does occur, and illustrates the processes that created Earth's biodiversity. It supports the modern evolutionary synthesis—the current scientific theory that explains how and why life changes over time. Evolutionary biologists document evidence of common descent, all the way back to the last universal common ancestor, by developing testable predictions, testing hypotheses, and constructing theories that illustrate and describe its causes.
Comparison of the DNA genetic sequences of organisms has revealed that organisms that are phylogenetically close have a higher degree of DNA sequence similarity than organisms that are phylogenetically distant. Genetic fragments such as pseudogenes, regions of DNA that are orthologous to a gene in a related organism, but are no longer active and appear to be undergoing a steady process of degeneration from cumulative mutations support common descent alongside the universal biochemical organization and molecular variance patterns found in all organisms. Additional genetic information conclusively supports the relatedness of life and has allowed scientists (since the discovery of DNA) to develop phylogenetic trees: a construction of organisms' evolutionary relatedness. It has also led to the development of molecular clock techniques to date taxon divergence times and to calibrate these with the fossil record.
Fossils are important for estimating when various lineages developed in geologic time. As fossilization is an uncommon occurrence, usually requiring hard body parts and death near a site where sediments are being deposited, the fossil record only provides sparse and intermittent information about the evolution of life. Evidence of organisms prior to the development of hard body parts such as shells, bones and teeth is especially scarce, but exists in the form of ancient microfossils, as well as impressions of various soft-bodied organisms. The comparative study of the anatomy of groups of animals shows structural features that are fundamentally similar (homologous), demonstrating phylogenetic and ancestral relationships with other organisms, most especially when compared with fossils of ancient extinct organisms. Vestigial structures and comparisons in embryonic development are largely a contributing factor in anatomical resemblance in concordance with common descent. Since metabolic processes do not leave fossils, research into the evolution of the basic cellular processes is done largely by comparison of existing organisms' physiology and biochemistry. Many lineages diverged at different stages of development, so it is possible to determine when certain metabolic processes appeared by comparing the traits of the descendants of a common ancestor.
Evidence from animal coloration was gathered by some of Darwin's contemporaries; camouflage, mimicry, and warning coloration are all readily explained by natural selection. Special cases like the seasonal changes in the plumage of the ptarmigan, camouflaging it against snow in winter and against brown moorland in summer provide compelling evidence that selection is at work. Further evidence comes from the field of biogeography because evolution with common descent provides the best and most thorough explanation for a variety of facts concerning the geographical distribution of plants and animals across the world. This is especially obvious in the field of insular biogeography. Combined with the well-established geological theory of plate tectonics, common descent provides a way to combine facts about the current distribution of species with evidence from the fossil record to provide a logically consistent explanation of how the distribution of living organisms has changed over time.
The development and spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria provides evidence that evolution due to natural selection is an ongoing process in the natural world. Natural selection is ubiquitous in all research pertaining to evolution, taking note of the fact that all of the following examples in each section of the article document the process. Alongside this are observed instances of the separation of populations of species into sets of new species (speciation). Speciation has been observed in the lab and in nature. Multiple forms of such have been described and documented as examples for individual modes of speciation. Furthermore, evidence of common descent extends from direct laboratory experimentation with the selective breeding of organisms—historically and currently—and other controlled experiments involving many of the topics in the article. This article summarizes the varying disciplines that provide the evidence for evolution and the common descent of all life on Earth, accompanied by numerous and specialized examples, indicating a compelling consilience of evidence.
Evidence from comparative physiology and biochemistry[edit]
Genetics[edit]
One of the strongest evidences for common descent comes from gene sequences. Comparative sequence analysis examines the relationship between the DNA sequences of different species,[1] producing several lines of evidence that confirm Darwin's original hypothesis of common descent. If the hypothesis of common descent is true, then species that share a common ancestor inherited that ancestor's DNA sequence, as well as mutations unique to that ancestor. More closely related species have a greater fraction of identical sequence and shared substitutions compared to more distantly related species.

The simplest and most powerful evidence is provided by phylogenetic reconstruction. Such reconstructions, especially when done using slowly evolving protein sequences, are often quite robust and can be used to reconstruct a great deal of the evolutionary history of modern organisms (and even in some instances of the evolutionary history of extinct organisms, such as the recovered gene sequences of mammoths or Neanderthals). These reconstructed phylogenies recapitulate the relationships established through morphological and biochemical studies.[2] The most detailed reconstructions have been performed on the basis of the mitochondrial genomes shared by all eukaryotic organisms,[3] which are short and easy to sequence; the broadest reconstructions have been performed either using the sequences of a few very ancient proteins or by using ribosomal RNA sequence.[citation needed]
Phylogenetic relationships extend to a wide variety of nonfunctional sequence elements, including repeats, transposons, pseudogenes, and mutations in protein-coding sequences that do not change the amino-acid sequence. While a minority of these elements might later be found to harbor function, in aggregate they demonstrate that identity must be the product of common descent rather than common function.[4]
Universal biochemical organisation and molecular variance patterns[edit]
All known extant (surviving) organisms are based on the same biochemical processes: genetic information encoded as nucleic acid (DNA, or RNA for many viruses), transcribed into RNA, then translated into proteins (that is, polymers of amino acids) by highly conserved ribosomes. Perhaps most tellingly, the Genetic Code (the "translation table" between DNA and amino acids) is the same for almost every organism, meaning that a piece of DNA in a bacterium codes for the same amino acid as in a human cell. ATP is used as energy currency by all extant life. A deeper understanding of developmental biology shows that common morphology is, in fact, the product of shared genetic elements.[5] For example, although camera-like eyes are believed to have evolved independently on many separate occasions,[6] they share a common set of light-sensing proteins (opsins), suggesting a common point of origin for all sighted creatures.[7][8] Another example is the familiar vertebrate body plan, whose structure is controlled by the homeobox (Hox) family of genes.[9]
DNA sequencing[edit]
Comparison of DNA sequences allows organisms to be grouped by sequence similarity, and the resulting phylogenetic trees are typically congruent with traditional taxonomy, and are often used to strengthen or correct taxonomic classifications. Sequence comparison is considered a measure robust enough to correct erroneous assumptions in the phylogenetic tree in instances where other evidence is scarce. For example, neutral human DNA sequences are approximately 1.2% divergent (based on substitutions) from those of their nearest genetic relative, the chimpanzee, 1.6% from gorillas, and 6.6% from baboons.[10][11] Genetic sequence evidence thus allows inference and quantification of genetic relatedness between humans and other apes.[12][13] The sequence of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene, a vital gene encoding a part of the ribosome, was used to find the broad phylogenetic relationships between all extant life. The analysis by Carl Woese resulted in the three-domain system, arguing for two major splits in the early evolution of life. The first split led to modern Bacteria and the subsequent split led to modern Archaea and Eukaryotes.[14][15]
Some DNA sequences are shared by very different organisms. It has been predicted by the theory of evolution that the differences in such DNA sequences between two organisms should roughly resemble both the biological difference between them according to their anatomy and the time that had passed since these two organisms have separated in the course of evolution, as seen in fossil evidence. The rate of accumulating such changes should be low for some sequences, namely those that code for critical RNA or proteins, and high for others that code for less critical RNA or proteins; but for every specific sequence, the rate of change should be roughly constant over time. These results have been experimentally confirmed. Two examples are DNA sequences coding for rRNA, which is highly conserved, and DNA sequences coding for fibrinopeptides, amino acid chains discarded during the formation of fibrin, which are highly non-conserved.[16]
Proteins[edit]
Proteomic evidence also supports the universal ancestry of life. Vital proteins, such as the ribosome, DNA polymerase, and RNA polymerase, are found in everything from the most primitive bacteria to the most complex mammals. The core part of the protein is conserved across all lineages of life, serving similar functions. Higher organisms have evolved additional protein subunits, largely affecting the regulation and protein-protein interaction of the core. Other overarching similarities between all lineages of extant organisms, such as DNA, RNA, amino acids, and the lipid bilayer, give support to the theory of common descent. Phylogenetic analyses of protein sequences from various organisms produce similar trees of relationship between all organisms.[17] The chirality of DNA, RNA, and amino acids is conserved across all known life. As there is no functional advantage to right- or left-handed molecular chirality, the simplest hypothesis is that the choice was made randomly by early organisms and passed on to all extant life through common descent. Further evidence for reconstructing ancestral lineages comes from junk DNA such as pseudogenes, "dead" genes that steadily accumulate mutations.[18]
Pseudogenes[edit]
Pseudogenes, also known as noncoding DNA, are extra DNA in a genome that do not get transcribed into RNA to synthesize proteins. Some of this noncoding DNA has known functions, but much of it has no known function and is called "Junk DNA".[19][20][21][22] This is an example of a vestige since replicating these genes uses energy, making it a waste in many cases. A pseudogene can be produced when a coding gene accumulates mutations that prevent it from being transcribed, making it non-functional.[19] But since it is not transcribed, it may disappear without affecting fitness, unless it has provided some beneficial function as non-coding DNA. Non-functional pseudogenes may be passed on to later species, thereby labeling the later species as descended from the earlier species.[citation needed]
Other mechanisms[edit]
A large body of molecular evidence supports a variety of mechanisms for large evolutionary changes, including: genome and gene duplication, which facilitates rapid evolution by providing substantial quantities of genetic material under weak or no selective constraints; horizontal gene transfer, the process of transferring genetic material to another cell that is not an organism's offspring, allowing for species to acquire beneficial genes from each other; and recombination, capable of reassorting large numbers of different alleles and of establishing reproductive isolation. The endosymbiotic theory explains the origin of mitochondria and plastids (including chloroplasts), which are organelles of eukaryotic cells, as the incorporation of an ancient prokaryotic cell into ancient eukaryotic cell. Rather than evolving eukaryotic organelles slowly, this theory offers a mechanism for a sudden evolutionary leap by incorporating the genetic material and biochemical composition of a separate species. Evidence supporting this mechanism has been found in the protist Hatena: as a predator it engulfs a green algal cell, which subsequently behaves as an endosymbiont, nourishing Hatena, which in turn loses its feeding apparatus and behaves as an autotroph.[23][24]
Since metabolic processes do not leave fossils, research into the evolution of the basic cellular processes is done largely by comparison of existing organisms. Many lineages diverged when new metabolic processes appeared, and it is theoretically possible to determine when certain metabolic processes appeared by comparing the traits of the descendants of a common ancestor or by detecting their physical manifestations. As an example, the appearance of oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere is linked to the evolution of photosynthesis.[original research?][citation needed]
Specific examples from comparative physiology and biochemistry[edit]
Chromosome 2 in humans[edit]
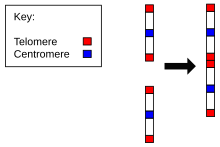
Evidence for the evolution of Homo sapiens from a common ancestor with chimpanzees is found in the number of chromosomes in humans as compared to all other members of Hominidae. All hominidae have 24 pairs of chromosomes, except humans, who have only 23 pairs. Human chromosome 2 is a result of an end-to-end fusion of two ancestral chromosomes.[25][26]
The evidence for this includes:
- The correspondence of chromosome 2 to two ape chromosomes. The closest human relative, the chimpanzee, has near-identical DNA sequences to human chromosome 2, but they are found in two separate chromosomes. The same is true of the more distant gorilla and orangutan.[27][28]
- The presence of a vestigial centromere. Normally a chromosome has just one centromere, but in chromosome 2 there are remnants of a second centromere.[29]
- The presence of vestigial telomeres. These are normally found only at the ends of a chromosome, but in chromosome 2 there are additional telomere sequences in the middle.[30]
Chromosome 2 thus presents strong evidence in favour of the common descent of humans and other apes. According to J. W. Ijdo, "We conclude that the locus cloned in cosmids c8.1 and c29B is the relic of an ancient telomere-telomere fusion and marks the point at which two ancestral ape chromosomes fused to give rise to human chromosome 2."[30]
Cytochrome c and b[edit]
A classic example of biochemical evidence for evolution is the variance of the ubiquitous (i.e. all living organisms have it, because it performs very basic life functions) protein Cytochrome c in living cells. The variance of cytochrome c of different organisms is measured in the number of differing amino acids, each differing amino acid being a result of a base pair substitution, a mutation. If each differing amino acid is assumed the result of one base pair substitution, it can be calculated how long ago the two species diverged by multiplying the number of base pair substitutions by the estimated time it takes for a substituted base pair of the cytochrome c gene to be successfully passed on. For example, if the average time it takes for a base pair of the cytochrome c gene to mutate is N years, the number of amino acids making up the cytochrome c protein in monkeys differ by one from that of humans, this leads to the conclusion that the two species diverged N years ago.
The primary structure of cytochrome c consists of a chain of about 100 amino acids. Many higher order organisms possess a chain of 104 amino acids.[31]
The cytochrome c molecule has been extensively studied for the glimpse it gives into evolutionary biology. Both chicken and turkeys have identical sequence homology (amino acid for amino acid), as do pigs, cows and sheep. Both humans and chimpanzees share the identical molecule, while rhesus monkeys share all but one of the amino acids:[32] the 66th amino acid is isoleucine in the former and threonine in the latter.[31]
What makes these homologous similarities particularly suggestive of common ancestry in the case of cytochrome c, in addition to the fact that the phylogenies derived from them match other phylogenies very well, is the high degree of functional redundancy of the cytochrome c molecule. The different existing configurations of amino acids do not significantly affect the functionality of the protein, which indicates that the base pair substitutions are not part of a directed design, but the result of random mutations that are not subject to selection.[33]
In addition, Cytochrome b is commonly used as a region of mitochondrial DNA to determine phylogenetic relationships between organisms due to its sequence variability. It is considered most useful in determining relationships within families and genera. Comparative studies involving cytochrome b have resulted in new classification schemes and have been used to assign newly described species to a genus, as well as deepen the understanding of evolutionary relationships.[34]
Endogenous retroviruses[edit]
Endogenous retroviruses (or ERVs) are remnant sequences in the genome left from ancient viral infections in an organism. The retroviruses (or virogenes) are always passed on to the next generation of that organism that received the infection. This leaves the virogene left in the genome. Because this event is rare and random, finding identical chromosomal positions of a virogene in two different species suggests common ancestry.[33] Cats (Felidae) present a notable instance of virogene sequences demonstrating common descent. The standard phylogenetic tree for Felidae have smaller cats (Felis chaus, Felis silvestris, Felis nigripes, and Felis catus) diverging from larger cats such as the subfamily Pantherinae and other carnivores. The fact that small cats have an ERV where the larger cats do not suggests that the gene was inserted into the ancestor of the small cats after the larger cats had diverged.[35] Another example of this is with humans and chimps. Humans contain numerous ERVs that comprise a considerable percentage of the genome. Sources vary, but 1%[36] to 8%[37] has been proposed. Humans and chimps share seven different occurrences of virogenes, while all primates share similar retroviruses congruent with phylogeny.[38][39]
Recent African origin of modern humans[edit]
Mathematical models of evolution, pioneered by the likes of Sewall Wright, Ronald Fisher and J. B. S. Haldane and extended via diffusion theory by Motoo Kimura, allow predictions about the genetic structure of evolving populations. Direct examination of the genetic structure of modern populations via DNA sequencing has allowed verification of many of these predictions. For example, the Out of Africa theory of human origins, which states that modern humans developed in Africa and a small sub-population migrated out (undergoing a population bottleneck), implies that modern populations should show the signatures of this migration pattern. Specifically, post-bottleneck populations (Europeans and Asians) should show lower overall genetic diversity and a more uniform distribution of allele frequencies compared to the African population. Both of these predictions are borne out by actual data from a number of studies.[40]
Evidence from comparative anatomy[edit]
Comparative study of the anatomy of groups of animals or plants reveals that certain structural features are basically similar. For example, the basic structure of all flowers consists of sepals, petals, stigma, style and ovary; yet the size, colour, number of parts and specific structure are different for each individual species. The neural anatomy of fossilized remains may also be compared using advanced imaging techniques.[41]
Atavisms[edit]

Once thought of as a refutation to evolutionary theory, atavisms are "now seen as potent evidence of how much genetic potential is retained...after a particular structure has disappeared from a species".[43] "Atavisms are the reappearance of a lost character typical of remote ancestors and not seen in the parents or recent ancestors..."[44] and are an "[indication] of the developmental plasticity that exists within embryos..."[44] Atavisms occur because genes for previously existing phenotypical features are often preserved in DNA, even though the genes are not expressed in some or most of the organisms possessing them.[45] Numerous examples have documented the occurrence of atavisms alongside experimental research triggering their formation. Due to the complexity and interrelatedness of the factors involved in the development of atavisms, both biologists and medical professionals find it "difficult, if not impossible, to distinguish [them] from malformations."[46]
Some examples of atavisms found in the scientific literature include:
- Hind limbs in whales.[44] (see figure 2a)
- Reappearance of limbs in limbless vertebrates.[43][44][47]
- Back pair of flippers on a bottlenose dolphin.[48]
- Extra toes of the modern horse.[44][49][50]
- Human tails (not pseudo-tails)[46][51] and extra nipples in humans.[44]
- Re-evolution of sexuality from parthenogenesis in orbitid mites.[52]
- Teeth in chickens.[53]
- Dewclaws in dogs.[44]
- Reappearance of wings on wingless stick insects[54] and earwigs.[44]
- Atavistic muscles in several birds[55][56] and mammals such as the beagle[57] and the jerboa.[55]
- Extra toes in guinea pigs.[44][58]
Evolutionary developmental biology and embryonic development[edit]
Evolutionary developmental biology is the biological field that compares the developmental process of different organisms to determine ancestral relationships between species. A large variety of organism's genomes contain a small fraction of genes that control the organisms development. Hox genes are an example of these types of nearly universal genes in organisms pointing to an origin of common ancestry. Embryological evidence comes from the development of organisms at the embryological level with the comparison of different organisms embryos similarity. Remains of ancestral traits often appear and disappear in different stages of the embryological development process.
Some examples include:
- Hair growth and loss (lanugo) during human development.[59]
- Development and degeneration of a yolk sac.
- Terrestrial frogs and salamanders passing through the larval stage within the egg—with features of typically aquatic larvae—but hatch ready for life on land;[60]
- The appearance of gill-like structures (pharyngeal arch) in vertebrate embryo development. Note that in fish, the arches continue to develop as branchial arches while in humans, for example, they give rise to a variety of structures within the head and neck.
Homologous structures and divergent (adaptive) evolution[edit]
If widely separated groups of organisms are originated from a common ancestry, they are expected to have certain basic features in common. The degree of resemblance between two organisms should indicate how closely related they are in evolution:
- Groups with little in common are assumed to have diverged from a common ancestor much earlier in geological history than groups with a lot in common;
- In deciding how closely related two animals are, a comparative anatomist looks for structures that are fundamentally similar, even though they may serve different functions in the adult. Such structures are described as homologous and suggest a common origin.
- In cases where the similar structures serve different functions in adults, it may be necessary to trace their origin and embryonic development. A similar developmental origin suggests they are the same structure, and thus likely derived from a common ancestor.
When a group of organisms share a homologous structure that is specialized to perform a variety of functions to adapt different environmental conditions and modes of life, it is called adaptive radiation. The gradual spreading of organisms with adaptive radiation is known as divergent evolution.
Nested hierarchies and classification[edit]
Taxonomy is based on the fact that all organisms are related to each other in nested hierarchies based on shared characteristics. Most existing species can be organized rather easily in a nested hierarchical classification. This is evident from the Linnaean classification scheme. Based on shared derived characters, closely related organisms can be placed in one group (such as a genus), several genera can be grouped together into one family, several families can be grouped together into an order, etc.[61] The existence of these nested hierarchies was recognized by many biologists before Darwin, but he showed that his theory of evolution with its branching pattern of common descent could explain them.[61][62] Darwin described how common descent could provide a logical basis for classification:[63]
All the foregoing rules and aids and difficulties in classification are explained, if I do not greatly deceive myself, on the view that the natural system is founded on descent with modification; that the characters which naturalists consider as showing true affinity between any two or more species, are those which have been inherited from a common parent, and, in so far, all true classification is genealogical; that community of descent is the hidden bond which naturalists have been unconsciously seeking, ...
— Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, page 577
Evolutionary trees[edit]
An evolutionary tree (of Amniota, for example, the last common ancestor of mammals and reptiles, and all its descendants) illustrates the initial conditions causing evolutionary patterns of similarity (e.g., all Amniotes produce an egg that possesses the amnios) and the patterns of divergence amongst lineages (e.g., mammals and reptiles branching from the common ancestry in Amniota). Evolutionary trees provide conceptual models of evolving systems once thought limited in the domain of making predictions out of the theory.[64] However, the method of phylogenetic bracketing is used to infer predictions with far greater probability than raw speculation. For example, paleontologists use this technique to make predictions about nonpreservable traits in fossil organisms, such as feathered dinosaurs, and molecular biologists use the technique to posit predictions about RNA metabolism and protein functions.[65][66] Thus evolutionary trees are evolutionary hypotheses that refer to specific facts, such as the characteristics of organisms (e.g., scales, feathers, fur), providing evidence for the patterns of descent, and a causal explanation for modification (i.e., natural selection or neutral drift) in any given lineage (e.g., Amniota). Evolutionary biologists test evolutionary theory using phylogenetic systematic methods that measure how much the hypothesis (a particular branching pattern in an evolutionary tree) increases the likelihood of the evidence (the distribution of characters among lineages).[67][68][69] The severity of tests for a theory increases if the predictions "are the least probable of being observed if the causal event did not occur."[70] "Testability is a measure of how much the hypothesis increases the likelihood of the evidence."[71]
Vestigial structures[edit]
Evidence for common descent comes from the existence of vestigial structures.[72] These rudimentary structures are often homologous to structures that correspond in related or ancestral species. A wide range of structures exist such as mutated and non-functioning genes, parts of a flower, muscles, organs, and even behaviors. This variety can be found across many different groups of species. In many cases they are degenerated or underdeveloped. The existence of vestigial organs can be explained in terms of changes in the environment or modes of life of the species. Those organs are typically functional in the ancestral species but are now either semi-functional, nonfunctional, or re-purposed.
Scientific literature concerning vestigial structures abounds. One study compiled 64 examples of vestigial structures found in the literature across a wide range of disciplines within the 21st century.[73] The following non-exhaustive list summarizes Senter et al. alongside various other examples:
- The presence of remnant mitochondria (mitosomes) that have lost the ability to synthesize ATP in Entamoeba histolytica, Trachipleistophora hominis, Cryptosporidium parvum, Blastocystis hominis, and Giardia intestinalis.[74]
- Remnant chloroplast organelles (leucoplasts) in non-photosynthetic algae species (Plasmodium falciparum, Toxoplasma gondii, Aspasia longa, Anthophysa vegetans, Ciliophrys infusionum, Pteridomonas danica, Paraphysomonas, Spumella and Epifagus americana.[75]
- Missing stamens (unvascularized staminodes) on Gilliesia and Gethyum flowers.[76]
- Non-functioning androecium in female flowers and non-functioning gynoecium in male flowers of the cactus species Consolea spinosissima.[77]
- Remnant stamens on female flowers of Fragaria virginiana;[78] all species in the genus Schiedea;[79] and on Penstemon centranthifolius, P. rostriflorus, P. ellipticus, and P. palmeri.[80]
- Vestigial anthers on Nemophila menziesii.[81]

- Reduced hindlimbs and pelvic girdle embedded in the muscles of extant whales (see figure 2b).[82][83][84][85] Occasionally, the genes that code for longer extremities cause a modern whale to develop legs. On 28 October 2006, a four-finned bottlenose dolphin was caught and studied due to its extra set of hind limbs.[86] These legged Cetacea display an example of an atavism predicted from their common ancestry.
- Nonfunctional hind wings in Carabus solieri[87] and other beetles.[83]
- Remnant eyes (and eye structures) in animals that have lost sight such as blind cavefish (e.g. Astyanax mexicanus),[88] mole rats, snakes, spiders, salamanders, shrimp, crayfish, and beetles.[89][90]
- Vestigial eye in the extant Rhineura floridana and remnant jugal in the extinct Rhineura hatchery (reclassified as Protorhineura hatcherii).[91][92]
- Functionless wings in flightless birds such as ostriches, kiwis, cassowaries, and emus.[93][94]
- The presence of the plica semilunaris in the human eye—a vestigial remnant of the nictitating membrane.[95]
- Harderian gland in primates.[96]
- Reduced hind limbs and pelvic girdle structures in legless lizards, skinks,[97] amphisbaenians, and some snakes.[98][99]
- Reduced and missing olfactory apparatus in whales that still possess vestigial olfactory receptor subgenomes.[100]
- Vestigial teeth in narwhal.[101]
- Rudimentary digits of Ateles geoffroyi, Colobus guereza, and Perodicticus potto.[102]
- Vestigial dental primordia in the embryonic tooth pattern in mice.[103]
- Reduced or absent vomeronasal organ in humans and Old World monkeys.[104][105]
- Presence of non-functional sinus hair muscles in humans used in whisker movement.[106]
- Degenerating palmaris longus muscle in humans.[107]
- Teleost fish, anthropoid primates (Simians), guinea pigs, some bat species, and some Passeriformes have lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C (ascorbic acid), yet still possess the genes involved. This inability is due to mutations of the L-gulono-γ-lactone oxidase (GLO) gene— and in primates, teleost fish, and guinea pigs it is irreversible.[108]
- Remnant abdominal segments in cirripedes (barnacles).[109]
- Non-mammalian vertebrate embryos depend on nutrients from the yolk sac. Humans and other mammal genomes contain broken, non-functioning genes that code for the production of yolk. alongside the presence of an empty yolk sac with the embryo.[110][111][112]
- Dolphin embryonic limb buds.[113]
- Leaf formation in some cacti species.[114]
- Presence of a vestigial endosymbiont Lepidodinium viride within the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium chlorophorum.[115]
- The species Dolabrifera dolabrifera has an ink gland but is "incapable of producing ink or its associated anti-predator proteins".[116]
Specific examples from comparative anatomy[edit]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2021) |
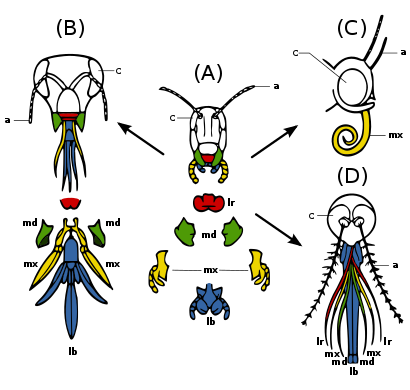
(A) Primitive state — biting and chewing: e.g. grasshopper. Strong mandibles and maxillae for manipulating food.
(B) Ticking and biting: e.g. honey bee. Labium long to lap up nectar; mandibles chew pollen and mould wax.
(C) Sucking: e.g. butterfly. Labrum reduced; mandibles lost; maxillae long forming sucking tube.
(D) Piercing and sucking, e.g.. female mosquito. Labrum and maxillae form tube; mandibles form piercing stylets; labrum grooved to hold other parts.
Insect mouthparts and appendages[edit]
Many different species of insects have mouthparts derived from the same embryonic structures, indicating that the mouthparts are modifications of a common ancestor's original features. These include a labrum (upper lip), a pair of mandibles, a hypopharynx (floor of mouth), a pair of maxillae, and a labium. (Fig. 2c) Evolution has caused enlargement and modification of these structures in some species, while it has caused the reduction and loss of them in other species. The modifications enable the insects to exploit a variety of food materials.
Insect mouthparts and antennae are considered homologues of insect legs. Parallel developments are seen in some arachnids: The anterior pair of legs may be modified as analogues of antennae, particularly in whip scorpions, which walk on six legs. These developments provide support for the theory that complex modifications often arise by duplication of components, with the duplicates modified in different directions.
Pelvic structure of dinosaurs[edit]
Similar to the pentadactyl limb in mammals, the earliest dinosaurs split into two distinct orders—the saurischia and ornithischia. They are classified as one or the other in accordance with what the fossils demonstrate. Figure 2d, shows that early saurischians resembled early ornithischians. The pattern of the pelvis in all species of dinosaurs is an example of homologous structures. Each order of dinosaur has slightly differing pelvis bones providing evidence of common descent. Additionally, modern birds show a similarity to ancient saurischian pelvic structures indicating the evolution of birds from dinosaurs. This can also be seen in Figure 5c as the Aves branch off the Theropoda suborder.
Pentadactyl limb[edit]
The pattern of limb bones called pentadactyl limb is an example of homologous structures (Fig. 2e). It is found in all classes of tetrapods (i.e. from amphibians to mammals). It can even be traced back to the fins of certain fossil fishes from which the first amphibians evolved such as tiktaalik. The limb has a single proximal bone (humerus), two distal bones (radius and ulna), a series of carpals (wrist bones), followed by five series of metacarpals (palm bones) and phalanges (digits). Throughout the tetrapods, the fundamental structures of pentadactyl limbs are the same, indicating that they originated from a common ancestor. But in the course of evolution, these fundamental structures have been modified. They have become superficially different and unrelated structures to serve different functions in adaptation to different environments and modes of life. This phenomenon is shown in the forelimbs of mammals. For example:
- In monkeys, the forelimbs are much elongated, forming a grasping hand used for climbing and swinging among trees.
- Pigs have lost their first digit, while the second and fifth digits are reduced. The remaining two digits are longer and stouter than the rest and bear a hoof for supporting the body.
- In horses, the forelimbs are highly adapted for strength and support. Fast and long-distance running is possible due to the extensive elongation of the third digit that bears a hoof.
- The mole has a pair of short, spade-like forelimbs for burrowing.
- Anteaters use their enlarged third digit for tearing into ant and termite nests.
- In cetaceans, the forelimbs become flippers for steering and maintaining equilibrium during swimming.
- In bats, the forelimbs have become highly modified and evolved into functioning wings. Four digits have become elongated, while the hook-like first digit remains free and is used to grip.
Recurrent laryngeal nerve in giraffes[edit]
The recurrent laryngeal nerve is a fourth branch of the vagus nerve, which is a cranial nerve. In mammals, its path is unusually long. As a part of the vagus nerve, it comes from the brain, passes through the neck down to heart, rounds the dorsal aorta and returns up to the larynx, again through the neck. (Fig. 2f)
This path is suboptimal even for humans, but for giraffes it becomes even more suboptimal. Due to the lengths of their necks, the recurrent laryngeal nerve may be up to 4 m (13 ft) long, despite its optimal route being a distance of just several inches.
The indirect route of this nerve is the result of evolution of mammals from fish, which had no neck and had a relatively short nerve that innervated one gill slit and passed near the gill arch. Since then, the gill it innervated has become the larynx and the gill arch has become the dorsal aorta in mammals.[117][118]
Route of the vas deferens[edit]
Similar to the laryngeal nerve in giraffes, the vas deferens is part of the male anatomy of many vertebrates; it transports sperm from the epididymis in anticipation of ejaculation. In humans, the vas deferens routes up from the testicle, looping over the ureter, and back down to the urethra and penis. It has been suggested that this is due to the descent of the testicles during the course of human evolution—likely associated with temperature. As the testicles descended, the vas deferens lengthened to accommodate the accidental "hook" over the ureter.[118][119]
Evidence from paleontology[edit]
When organisms die, they often decompose rapidly or are consumed by scavengers, leaving no permanent evidences of their existence. However, occasionally, some organisms are preserved. The remains or traces of organisms from a past geologic age embedded in rocks by natural processes are called fossils. They are extremely important for understanding the evolutionary history of life on Earth, as they provide direct evidence of evolution and detailed information on the ancestry of organisms. Paleontology is the study of past life based on fossil records and their relations to different geologic time periods.
For fossilization to take place, the traces and remains of organisms must be quickly buried so that weathering and decomposition do not occur. Skeletal structures or other hard parts of the organisms are the most commonly occurring form of fossilized remains. There are also some trace "fossils" showing moulds, cast or imprints of some previous organisms.
As an animal dies, the organic materials gradually decay, such that the bones become porous. If the animal is subsequently buried in mud, mineral salts infiltrate into the bones and gradually fill up the pores. The bones harden into stones and are preserved as fossils. This process is known as petrification. If dead animals are covered by wind-blown sand, and if the sand is subsequently turned into mud by heavy rain or floods, the same process of mineral infiltration may occur. Apart from petrification, the dead bodies of organisms may be well preserved in ice, in hardened resin of coniferous trees (figure 3a), in tar, or in anaerobic, acidic peat. Fossilization can sometimes be a trace, an impression of a form. Examples include leaves and footprints, the fossils of which are made in layers that then harden.
Fossil record[edit]
It is possible to decipher how a particular group of organisms evolved by arranging its fossil record in a chronological sequence. Such a sequence can be determined because fossils are mainly found in sedimentary rock. Sedimentary rock is formed by layers of silt or mud on top of each other; thus, the resulting rock contains a series of horizontal layers, or strata. Each layer contains fossils typical for a specific time period when they formed. The lowest strata contain the oldest rock and the earliest fossils, while the highest strata contain the youngest rock and more recent fossils.
A succession of animals and plants can also be seen from fossil discoveries. By studying the number and complexity of different fossils at different stratigraphic levels, it has been shown that older fossil-bearing rocks contain fewer types of fossilized organisms, and they all have a simpler structure, whereas younger rocks contain a greater variety of fossils, often with increasingly complex structures.[121]
For many years, geologists could only roughly estimate the ages of various strata and the fossils found. They did so, for instance, by estimating the time for the formation of sedimentary rock layer by layer. Today, by measuring the proportions of radioactive and stable elements in a given rock, the ages of fossils can be more precisely dated by scientists. This technique is known as radiometric dating.
Throughout the fossil record, many species that appear at an early stratigraphic level disappear at a later level. This is interpreted in evolutionary terms as indicating the times when species originated and became extinct. Geographical regions and climatic conditions have varied throughout Earth's history. Since organisms are adapted to particular environments, the constantly changing conditions favoured species that adapted to new environments through the mechanism of natural selection.
Extent of the fossil record[edit]
Despite the relative rarity of suitable conditions for fossilization, an estimated 250,000 fossil species have been named.[122] The number of individual fossils this represents varies greatly from species to species, but many millions of fossils have been recovered: for instance, more than three million fossils from the last ice age have been recovered from the La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles.[123] Many more fossils are still in the ground, in various geological formations known to contain a high fossil density, allowing estimates of the total fossil content of the formation to be made. An example of this occurs in South Africa's Beaufort Formation (part of the Karoo Supergroup, which covers most of South Africa), which is rich in vertebrate fossils, including therapsids (reptile-mammal transitional forms).[124] It has been estimated that this formation contains 800 billion vertebrate fossils.[125] Palentologists have documented numerous transitional forms and have constructed "an astonishingly comprehensive record of the key transitions in animal evolution".[126] Conducting a survey of the paleontological literature, one would find that there is "abundant evidence for how all the major groups of animals are related, much of it in the form of excellent transitional fossils".[126]
Limitations[edit]
The fossil record is an important source for scientists when tracing the evolutionary history of organisms. However, because of limitations inherent in the record, there are not fine scales of intermediate forms between related groups of species. This lack of continuous fossils in the record is a major limitation in tracing the descent of biological groups. When transitional fossils are found that show intermediate forms in what had previously been a gap in knowledge, they are often popularly referred to as "missing links".
There is a gap of about 100 million years between the beginning of the Cambrian period and the end of the Ordovician period. The early Cambrian period was the period from which numerous fossils of sponges, cnidarians (e.g., jellyfish), echinoderms (e.g., eocrinoids), molluscs (e.g., snails) and arthropods (e.g., trilobites) are found. The first animal that possessed the typical features of vertebrates, the Arandaspis, was dated to have existed in the later Ordovician period. Thus few, if any, fossils of an intermediate type between invertebrates and vertebrates have been found, although likely candidates include the Burgess Shale animal, Pikaia gracilens,[127] and its Maotianshan shales relatives, Myllokunmingia, Yunnanozoon, Haikouella lanceolata,[128] and Haikouichthys.[129]
Some of the reasons for the incompleteness of fossil records are:
- In general, the probability that an organism becomes fossilized is very low;
- Some species or groups are less likely to become fossils because they are soft-bodied;
- Some species or groups are less likely to become fossils because they live (and die) in conditions that are not favourable for fossilization;
- Many fossils have been destroyed through erosion and tectonic movements;
- Most fossils are fragmentary;
- Some evolutionary change occurs in populations at the limits of a species' ecological range, and as these populations are likely small, the probability of fossilization is lower (see punctuated equilibrium);
- Similarly, when environmental conditions change, the population of a species is likely to be greatly reduced, such that any evolutionary change induced by these new conditions is less likely to be fossilized;
- Most fossils convey information about external form, but little about how the organism functioned;
- Using present-day biodiversity as a guide, this suggests that the fossils unearthed represent only a small fraction of the large number of species of organisms that lived in the past.
Specific examples from paleontology[edit]
Evolution of the horse[edit]
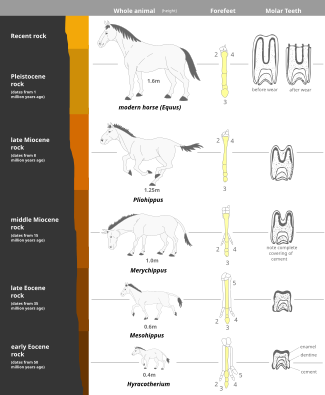
Due to an almost-complete fossil record found in North American sedimentary deposits from the early Eocene to the present, the horse provides one of the best examples of evolutionary history (phylogeny).
This evolutionary sequence starts with a small animal called Hyracotherium (commonly referred to as Eohippus), which lived in North America about 54 million years ago then spread across to Europe and Asia. Fossil remains of Hyracotherium show it to have differed from the modern horse in three important respects: it was a small animal (the size of a fox), lightly built and adapted for running; the limbs were short and slender, and the feet elongated so that the digits were almost vertical, with four digits in the forelimbs and three digits in the hindlimbs; and the incisors were small, the molars having low crowns with rounded cusps covered in enamel.[130]
The probable course of development of horses from Hyracotherium to Equus (the modern horse) involved at least 12 genera and several hundred species. The major trends seen in the development of the horse to changing environmental conditions may be summarized as follows:
- Increase in size (from 0.4 m to 1.5 m — from 15 in to 60 in);
- Lengthening of limbs and feet;
- Reduction of lateral digits;
- Increase in length and thickness of the third digit;
- Increase in width of incisors;
- Replacement of premolars by molars; and
- Increases in tooth length, crown height of molars.
Fossilized plants found in different strata show that the marshy, wooded country in which Hyracotherium lived became gradually drier. Survival now depended on the head being in an elevated position for gaining a good view of the surrounding countryside, and on a high turn of speed for escape from predators, hence the increase in size and the replacement of the splayed-out foot by the hoofed foot. The drier, harder ground would make the original splayed-out foot unnecessary for support. The changes in the teeth can be explained by assuming that the diet changed from soft vegetation to grass. A dominant genus from each geological period has been selected (see figure 3e) to show the slow alteration of the horse lineage from its ancestral to its modern form.[131]
Transition from fish to amphibians[edit]
Prior to 2004, paleontologists had found fossils of amphibians with necks, ears, and four legs, in rock no older than 365 million years old. In rocks more than 385 million years old they could only find fish, without these amphibian characteristics. Evolutionary theory predicted that since amphibians evolved from fish, an intermediate form should be found in rock dated between 365 and 385 million years ago. Such an intermediate form should have many fish-like characteristics, conserved from 385 million years ago or more, but also have many amphibian characteristics as well. In 2004, an expedition to islands in the Canadian arctic searching specifically for this fossil form in rocks that were 375 million years old discovered fossils of Tiktaalik.[132] Some years later, however, scientists in Poland found evidence of fossilised tetrapod tracks predating Tiktaalik.[133]
Evidence from biogeography[edit]
Data about the presence or absence of species on various continents and islands (biogeography) can provide evidence of common descent and shed light on patterns of speciation.
Continental distribution[edit]
All organisms are adapted to their environment to a greater or lesser extent. If the abiotic and biotic factors within a habitat are capable of supporting a particular species in one geographic area, then one might assume that the same species would be found in a similar habitat in a similar geographic area, e.g. in Africa and South America. This is not the case. Plant and animal species are discontinuously distributed throughout the world:
- Africa has Old World monkeys, apes, elephants, leopards, giraffes, and hornbills.
- South America has New World monkeys, cougars, jaguars, sloths, llamas, and toucans.
- Deserts in North and South America have native cacti, but deserts in Africa, Asia, and Australia have succulent (apart from Rhipsalis baccifera) which are native euphorbs that resemble cacti but are very different.[134]
Even greater differences can be found if Australia is taken into consideration, though it occupies the same latitude as much of South America and Africa. Marsupials like kangaroos, bandicoots, and quolls make up about half of Australia's indigenous mammal species.[135] By contrast, marsupials are today totally absent from Africa and form a smaller portion of the mammalian fauna of South America, where opossums, shrew opossums, and the monito del monte occur. The only living representatives of primitive egg-laying mammals (monotremes) are the echidnas and the platypus. The short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) and its subspecies populate Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea, and Kangaroo Island while the long-beaked echidna (Zaglossus bruijni) lives only in New Guinea. The platypus lives in the waters of eastern Australia. They have been introduced to Tasmania, King Island, and Kangaroo Island. These Monotremes are totally absent in the rest of the world.[136] On the other hand, Australia is missing many groups of placental mammals that are common on other continents (carnivorans, artiodactyls, shrews, squirrels, lagomorphs), although it does have indigenous bats and murine rodents; many other placentals, such as rabbits and foxes, have been introduced there by humans.[citation needed]
Other animal distribution examples include bears, located on all continents excluding Africa, Australia and Antarctica, and the polar bear solely in the Arctic Circle and adjacent land masses.[137] Penguins are found only around the South Pole despite similar weather conditions at the North Pole. Families of sirenians are distributed around the earth's waters, where manatees are located in western Africa waters, northern South American waters, and West Indian waters only while the related family, the dugongs, are located only in Oceanic waters north of Australia, and the coasts surrounding the Indian Ocean. The now extinct Steller's sea cow resided in the Bering Sea.[138]
The same kinds of fossils are found from areas known to be adjacent to one another in the past but that, through the process of continental drift, are now in widely divergent geographic locations. For example, fossils of the same types of ancient amphibians, arthropods and ferns are found in South America, Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica, which can be dated to the Paleozoic Era, when these regions were united as a single landmass called Gondwana.[139]
Island biogeography[edit]

Types of species found on islands[edit]
Evidence from island biogeography has played an important and historic role in the development of evolutionary biology. For purposes of biogeography, islands are divided into two classes. Continental islands are islands like Great Britain, and Japan that have at one time or another been part of a continent. Oceanic islands, like the Hawaiian islands, the Galápagos Islands and St. Helena, on the other hand are islands that have formed in the ocean and never been part of any continent. Oceanic islands have distributions of native plants and animals that are unbalanced in ways that make them distinct from the biotas found on continents or continental islands. Oceanic islands do not have native terrestrial mammals (they do sometimes have bats and seals), amphibians, or fresh water fish. In some cases they have terrestrial reptiles (such as the iguanas and giant tortoises of the Galápagos Islands) but often (such as in Hawaii) they do not. This is despite the fact that when species such as rats, goats, pigs, cats, mice, and cane toads, are introduced to such islands by humans they often thrive. Starting with Charles Darwin, many scientists have conducted experiments and made observations that have shown that the types of animals and plants found, and not found, on such islands are consistent with the theory that these islands were colonized accidentally by plants and animals that were able to reach them. Such accidental colonization could occur by air, such as plant seeds carried by migratory birds, or bats and insects being blown out over the sea by the wind, or by floating from a continent or other island by sea (for example, by some kinds of plant seeds like coconuts that can survive immersion in salt water), and reptiles that can survive for extended periods on rafts of vegetation carried to sea by storms.[140]
Endemism[edit]
Many of the species found on remote islands are endemic to a particular island or group of islands, meaning they are found nowhere else on earth. Examples of species endemic to islands include many flightless birds of New Zealand, lemurs of Madagascar, the Komodo dragon of Komodo,[141] the dragon's blood tree of Socotra,[142] Tuatara of New Zealand,[143][144] and others. However, many such endemic species are related to species found on other nearby islands or continents; the relationship of the animals found on the Galápagos Islands to those found in South America is a well-known example.[140] All of these facts, the types of plants and animals found on oceanic islands, the large number of endemic species found on oceanic islands, and the relationship of such species to those living on the nearest continents, are most easily explained if the islands were colonized by species from nearby continents that evolved into the endemic species now found there.[140]
Other types of endemism do not have to include, in the strict sense, islands. Islands can mean isolated lakes or remote and isolated areas. Examples of these would include the highlands of Ethiopia, Lake Baikal, fynbos of South Africa, forests of New Caledonia, and others. Examples of endemic organisms living in isolated areas include the kagu of New Caledonia,[145] cloud rats of the Luzon tropical pine forests of the Philippines,[146][147] the boojum tree (Fouquieria columnaris) of the Baja California peninsula,[148] and the Baikal seal.[149]
Adaptive radiations[edit]
Oceanic islands are frequently inhabited by clusters of closely related species that fill a variety of ecological niches, often niches that are filled by very different species on continents. Such clusters, like the finches of the Galápagos, Hawaiian honeycreepers, members of the sunflower family on the Juan Fernandez Archipelago and wood weevils on St. Helena are called adaptive radiations because they are best explained by a single species colonizing an island (or group of islands) and then diversifying to fill available ecological niches. Such radiations can be spectacular; 800 species of the fruit fly family Drosophila, nearly half the world's total, are endemic to the Hawaiian islands. Another illustrative example from Hawaii is the silversword alliance, which is a group of thirty species found only on those islands. Members range from the silverswords that flower spectacularly on high volcanic slopes to trees, shrubs, vines and mats that occur at various elevations from mountain top to sea level, and in Hawaiian habitats that vary from deserts to rainforests. Their closest relatives outside Hawaii, based on molecular studies, are tarweeds found on the west coast of North America. These tarweeds have sticky seeds that facilitate distribution by migrant birds.[150] Additionally, nearly all of the species on the island can be crossed and the hybrids are often fertile,[60] and they have been hybridized experimentally with two of the west coast tarweed species as well.[151] Continental islands have less distinct biota, but those that have been long separated from any continent also have endemic species and adaptive radiations, such as the 75 lemur species of Madagascar, and the eleven extinct moa species of New Zealand.[140][152]
Ring species[edit]
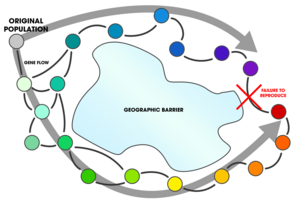
A ring species is a connected series of populations, each of which can interbreed with its neighbors, with at least two "end" populations which are too distantly related to interbreed, though with the potential for gene flow between all the populations.[153] Ring species represent speciation and have been cited as evidence of evolution. They illustrate what happens over time as populations genetically diverge, specifically because they represent, in living populations, what normally happens over time between long deceased ancestor populations and living populations, in which the intermediates have become extinct. Richard Dawkins says that ring species "are only showing us in the spatial dimension something that must always happen in the time dimension".[154]
Specific examples from biogeography[edit]
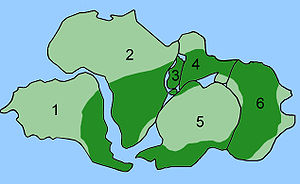
Distribution of Glossopteris[edit]
The combination of continental drift and evolution can sometimes be used to predict what will be found in the fossil record. Glossopteris is an extinct species of seed fern plants from the Permian. Glossopteris appears in the fossil record around the beginning of the Permian on the ancient continent of Gondwana.[155] Continental drift explains the current biogeography of the tree. Present day Glossopteris fossils are found in Permian strata in southeast South America, southeast Africa, all of Madagascar, northern India, all of Australia, all of New Zealand, and scattered on the southern and northern edges of Antarctica. During the Permian, these continents were connected as Gondwana (see figure 4c) in agreement with magnetic striping, other fossil distributions, and glacial scratches pointing away from the temperate climate of the South Pole during the Permian.[156][157]
Metatherian distribution[edit]
The history of metatherians (the clade containing marsupials and their extinct, primitive ancestors) provides an example of how evolutionary theory and the movement of continents can be combined to make predictions concerning fossil stratigraphy and distribution. The oldest metatherian fossils are found in present-day China.[158] Metatherians spread westward into modern North America (still attached to Eurasia) and then to South America, which was connected to North America until around 65 mya. Marsupials reached Australia via Antarctica about 50 mya, shortly after Australia had split off suggesting a single dispersion event of just one species.[159] Evolutionary theory suggests that the Australian marsupials descended from the older ones found in the Americas. Geologic evidence suggests that between 30 and 40 million years ago South America and Australia were still part of the Southern Hemisphere super continent of Gondwana and that they were connected by land that is now part of Antarctica. Therefore, when combining the models, scientists could predict that marsupials migrated from what is now South America, through Antarctica, and then to present-day Australia between 40 and 30 million years ago. A first marsupial fossil of the extinct family Polydolopidae was found on Seymour Island on the Antarctic Peninsula in 1982.[160] Further fossils have subsequently been found, including members of the marsupial orders Didelphimorphia (opossum) and Microbiotheria,[161] as well as ungulates and a member of the enigmatic extinct order Gondwanatheria, possibly Sudamerica ameghinoi.[162][163][164]
Migration, isolation, and distribution of the camel[edit]
The history of the camel provides an example of how fossil evidence can be used to reconstruct migration and subsequent evolution. The fossil record indicates that the evolution of camelids started in North America (see figure 4e), from which, six million years ago, they migrated across the Bering Strait into Asia and then to Africa, and 3.5 million years ago through the Isthmus of Panama into South America. Once isolated, they evolved along their own lines, giving rise to the Bactrian camel and dromedary in Asia and Africa and the llama and its relatives in South America. Camelids then became extinct in North America at the end of the last ice age.[165]
Evidence from selection[edit]
Scientists have observed and documented a multitude of events where natural selection is in action. The most well known examples are antibiotic resistance in the medical field along with better-known laboratory experiments documenting evolution's occurrence. Natural selection is tantamount to common descent in that long-term occurrence and selection pressures can lead to the diversity of life on earth as found today. All adaptations—documented and undocumented changes concerned—are caused by natural selection (and a few other minor processes). It is well established that, "...natural selection is a ubiquitous part of speciation...",[166] and is the primary driver of speciation.[167]
Artificial selection and experimental evolution[edit]

Artificial selection demonstrates the diversity that can exist among organisms that share a relatively recent common ancestor. In artificial selection, one species is bred selectively at each generation, allowing only those organisms that exhibit desired characteristics to reproduce. These characteristics become increasingly well developed in successive generations. Artificial selection was successful long before science discovered the genetic basis. Examples of artificial selection include dog breeding, genetically modified food, flower breeding, and the cultivation of foods such as wild cabbage,[168] and others.[citation needed]
Experimental evolution uses controlled experiments to test hypotheses and theories of evolution. In one early example, William Dallinger set up an experiment shortly before 1880, subjecting microbes to heat with the aim of forcing adaptive changes. His experiment ran for around seven years, and his published results were acclaimed, but he did not resume the experiment after the apparatus failed.[169]
A large-scale example of experimental evolution is Richard Lenski's multi-generation experiment with Escherichia coli. Lenski observed that some strains of E. coli evolved a complex new ability, the ability to metabolize citrate, after tens of thousands of generations.[170][171] The evolutionary biologist Jerry Coyne commented as a critique of creationism, saying, "the thing I like most is it says you can get these complex traits evolving by a combination of unlikely events. That's just what creationists say can't happen."[170] In addition to the metabolic changes, the different bacterial populations were found to have diverged in respect to both morphology (the overall size of the cell) and fitness (of which was measured in competition with the ancestors).[172]
Invertebrates[edit]
Historical lead tolerance in Daphnia[edit]
A study of species of Daphnia and lead pollution in the 20th century predicted that an increase in lead pollution would lead to strong selection of lead tolerance. Researchers were able to use "resurrection ecology", hatching decades-old Daphnia eggs from the time when lakes were heavily polluted with lead. The hatchlings in the study were compared to current-day Daphnia, and demonstrated "dramatic fitness differences between old and modern phenotypes when confronted with a widespread historical environmental stressor". Essentially, the modern-day Daphnia were unable to resist or tolerate high levels of lead (this is due to the huge reduction of lead pollution in 21st century lakes). The old hatchlings, however, were able to tolerate high lead pollution. The authors concluded that "by employing the techniques of resurrection ecology, we were able to show clear phenotypic change over decades...".[173]
Peppered moths[edit]
A classic example was the phenotypic change, light-to-dark color adaptation, in the peppered moth, due to pollution from the Industrial Revolution in England.[174][175]
Microbes[edit]
Antimicrobial resistance[edit]
The development and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is evidence for the process of evolution of species. Thus the appearance of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and the danger it poses to hospital patients, is a direct result of evolution through natural selection. The rise of Shigella strains resistant to the synthetic antibiotic class of sulfonamides also demonstrates the generation of new information as an evolutionary process.[176] Similarly, the appearance of DDT resistance in various forms of Anopheles mosquitoes, and the appearance of myxomatosis resistance in breeding rabbit populations in Australia, are both evidence of the existence of evolution in situations of evolutionary selection pressure in species in which generations occur rapidly.
All classes of microbes develop resistance: including fungi (antifungal resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), protozoa (antiprotozoal resistance), and bacteria (antibiotic resistance). This is to be expected when considering that all life exhibits universal genetic code and is therefore subject to the process of evolution through its various mechanisms.
Nylon-eating bacteria[edit]
Another example of organisms adapting to human-caused conditions are Nylon-eating bacteria: a strain of Flavobacterium that are capable of digesting certain byproducts of nylon 6 manufacturing. There is scientific consensus that the capacity to synthesize nylonase most probably developed as a single-step mutation that survived because it improved the fitness of the bacteria possessing the mutation. This is seen as a good example of evolution through mutation and natural selection that has been observed as it occurs and could not have come about until the production of nylon by humans.[177][178][179][180]
Plants and fungi[edit]
Monkeyflower radiation[edit]
Both subspecies Mimulus aurantiacus puniceus (red-flowered) and Mimulus aurantiacus australis (yellow-flowered) of monkeyflowers are isolated due to the preferences of their hummingbird and hawkmoth pollinators. The radiation of M. aurantiacus subspecies are mostly yellow colored; however, both M. a. ssp. puniceus and M. a. ssp. flemingii are red. Phylogenetic analysis suggests two independent origins of red-colored flowers that arose due to cis-regulatory mutations in the gene MaMyb2 that is present in all M. aurantiacus subspecies. Further research suggested that two independent mutations did not take place, but one MaMyb2 allele was transferred via introgressive hybridization.[181]
Radiotrophic fungi[edit]
Radiotrophic fungi is a perfect example of natural selection taking place after a chemical accident. Radiotrophic fungi appears to use the pigment melanin to convert gamma radiation into chemical energy for growth and were first discovered in 2007 as black molds growing inside and around the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant. Research at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine showed that three melanin-containing fungi, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, Wangiella dermatitidis, and Cryptococcus neoformans, increased in biomass and accumulated acetate faster in an environment in which the radiation level was 500 times higher than in the normal environment.[182][183]
Vertebrates[edit]
Guppies[edit]
While studying guppies (Poecilia reticulata) in Trinidad, biologist John Endler detected selection at work on the fish populations. To rule out alternative possibilities, Endler set up a highly controlled experiment to mimic the natural habitat by constructing ten ponds within a laboratory greenhouse at Princeton University. Each pond contained gravel to exactly match that of the natural ponds. After capturing a random sample of guppies from ponds in Trinidad, he raised and mixed them to create similar genetically diverse populations and measured each fish (spot length, spot height, spot area, relative spot length, relative spot height, total patch area, and standard body lengths). For the experiment he added Crenicichla alta (P. reticulata's main predator) in four of the ponds, Rivulus hartii (a non-predator fish) in four of the ponds, and left the remaining two ponds empty with only the guppies. After 10 generations, comparisons were made between each pond's guppy populations and measurements were taken again. Endler found that the populations had evolved dramatically different color patterns in the control and non-predator pools and drab color patterns in the predator pool. Predation pressure had caused a selection against standing out from background gravel.[184]

In parallel, during this experiment, Endler conducted a field experiment in Trinidad where he caught guppies from ponds where they had predators and relocated them to ponds upstream where the predators did not live. After 15 generations, Endler found that the relocated guppies had evolved dramatic and colorful patterns. Essentially, both experiments showed convergence due to similar selection pressures (i.e. predator selection against contrasting color patterns and sexual selection for contrasting color patterns).[184]
In a later study by David Reznick, the field population was examined 11 years later after Endler relocated the guppies to high streams. The study found that the populations has evolved in a number of different ways: bright color patterns, late maturation, larger sizes, smaller litter sizes, and larger offspring within litters.[185] Further studies of P. reticulata and their predators in the streams of Trinidad have indicated that varying modes of selection through predation have not only changed the guppies color patterns, sizes, and behaviors, but their life histories and life history patterns.[186]
Humans[edit]
Natural selection is observed in contemporary human populations, with recent findings demonstrating that the population at risk of the severe debilitating disease kuru has significant over-representation of an immune variant of the prion protein gene G127V versus non-immune alleles. Scientists postulate one of the reasons for the rapid selection of this genetic variant is the lethality of the disease in non-immune persons.[187][188] Other reported evolutionary trends in other populations include a lengthening of the reproductive period, reduction in cholesterol levels, blood glucose and blood pressure.[189]
A well known example of selection occurring in human populations is lactose tolerance. Lactose intolerance is the inability to metabolize lactose, because of a lack of the required enzyme lactase in the digestive system. The normal mammalian condition is for the young of a species to experience reduced lactase production at the end of the weaning period (a species-specific length of time). In humans, in non-dairy consuming societies, lactase production usually drops about 90% during the first four years of life, although the exact drop over time varies widely.[190] Lactase activity persistence in adults is associated with two polymorphisms: C/T 13910 and G/A 22018 located in the MCM6 gene.[191] This gene difference eliminates the shutdown in lactase production, making it possible for members of these populations to continue consumption of raw milk and other fresh and fermented dairy products throughout their lives without difficulty. This appears to be an evolutionarily recent (around 10,000 years ago [and 7,500 years ago in Europe][192]) adaptation to dairy consumption,[193] and has occurred independently in both northern Europe and east Africa in populations with a historically pastoral lifestyle.[194][195]
Italian wall lizards[edit]
In 1971, ten adult specimens of Podarcis sicula (the Italian wall lizard) were transported from the Croatian island of Pod Kopište to the island Pod Mrčaru (about 3.5 km to the east). Both islands lie in the Adriatic Sea near Lastovo, where the lizards founded a new bottlenecked population.[196][197] The two islands have similar size, elevation, microclimate, and a general absence of terrestrial predators[197] and the P. sicula expanded for decades without human interference, even out-competing the (now locally extinct[196]) Podarcis melisellensis population.[198]
In the 1990s, scientists returned to Pod Mrčaru and found that the lizards there differed greatly from those on Kopište. While mitochondrial DNA analyses have verified that P. sicula currently on Mrčaru are genetically very similar to the Kopište source population,[196] the new Mrčaru population of P. sicula had a larger average size, shorter hind limbs, lower maximal sprint speed and altered response to simulated predatory attacks compared to the original Kopište population.[197] These changes were attributed to "relaxed predation intensity" and greater protection from vegetation on Mrčaru.[197]
In 2008, further analysis revealed that the Mrčaru population of P. sicula have significantly different head morphology (longer, wider, and taller heads) and increased bite force compared to the original Kopište population.[196] This change in head shape corresponded with a shift in diet: Kopište P. sicula are primarily insectivorous, but those on Mrčaru eat substantially more plant matter.[196] The changes in foraging style may have contributed to a greater population density and decreased territorial behavior of the Mrčaru population.[196]
Another difference found between the two populations was the discovery, in the Mrčaru lizards, of cecal valves, which slow down food passage and provide fermenting chambers, allowing commensal microorganisms to convert cellulose to nutrients digestible by the lizards.[196] Additionally, the researchers discovered that nematodes were common in the guts of Mrčaru lizards, but absent from Kopište P. sicula, which do not have cecal valves.[196] The cecal valves, which occur in less than 1 percent of all known species of scaled reptiles,[196] have been described as an "adaptive novelty, a brand new feature not present in the ancestral population and newly evolved in these lizards".[199]
PAH resistance in killifish[edit]
A similar study was also done regarding the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) that pollute the waters of the Elizabeth River in Portsmouth, Virginia. This chemical is a product of creosote, a type of tar. The Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) has evolved a resistance to PAHs involving the AHR gene (the same gene involved in the tomcods). This particular study focused on the resistance to "acute toxicity and cardiac teratogenesis" caused by PAHs. that mutated within the tomcods in the Hudson River.[200]
PCB resistance in codfish[edit]
An example involving the direct observation of gene modification due to selection pressures is the resistance to PCBs in codfish. After General Electric dumped polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the Hudson River from 1947 through 1976, tomcods (Microgadus tomcod) living in the river were found to have evolved an increased resistance to the compound's toxic effects.[201] The tolerance to the toxins is due to a change in the coding section of specific gene. Genetic samples were taken from the cods from 8 different rivers in the New England region: the St. Lawrence River, Miramichi River, Margaree River, Squamscott River, Niantic River, the Shinnecock Basic, the Hudson River, and the Hackensack River. Genetic analysis found that in the population of tomcods in the four southernmost rivers, the gene AHR2 (aryl hydrocarbon receptor 2) was present as an allele with a difference of two amino acid deletions.[202] This deletion conferred a resistance to PCB in the fish species and was found in 99% of Hudson River tomcods, 92% in the Hackensack River, 6% in the Niantic River, and 5% in Shinnecock Bay.[202] This pattern along the sampled bodies of waters infers a direct correlation of selective pressures leading to the evolution of PCB resistance in Atlantic tomcod fish.[202]
Urban wildlife[edit]
Urban wildlife is a broad and easily observable case of human-caused selection pressure on wildlife. With the growth in human habitats, different animals have adapted to survive within these urban environments. These types of environments can exert selection pressures on organisms, often leading to new adaptations. For example, the weed Crepis sancta, found in France, has two types of seed, heavy and fluffy. The heavy ones land nearby to the parent plant, whereas fluffy seeds float further away on the wind. In urban environments, seeds that float far often land on infertile concrete. Within about 5–12 generations, the weed evolves to produce significantly heavier seeds than its rural relatives.[203][204] Other examples of urban wildlife are rock pigeons and species of crows adapting to city environments around the world; African penguins in Simon's Town; baboons in South Africa; and a variety of insects living in human habitations. Studies have been conducted and have found striking changes to animals' (more specifically mammals') behavior and physical brain size due to their interactions with human-created environments.[205][206]
White Sands lizards[edit]

Animals that exhibit ecotonal variations allow for research concerning the mechanisms that maintain population differentiation. A wealth of information about natural selection, genotypic, and phenotypic variation;[207][208] adaptation and ecomorphology;[209] and social signaling[210] has been acquired from the studies of three species of lizards located in the White Sands desert of New Mexico. Holbrookia maculata, Aspidoscelis inornatus, and Sceloporus undulatus exhibit ecotonal populations that match both the dark soils and the white sands in the region. Research conducted on these species has found significant phenotypic and genotypic differences between the dark and light populations due to strong selection pressures. For example, H. maculata exhibits the strongest phenotypic difference (matches best with the substrate) of the light colored population coinciding with the least amount of gene flow between the populations and the highest genetic differences when compared to the other two lizard species.[207]
New Mexico's White Sands are a recent geologic formation (approximately 6000 years old[210] to possibly 2000 years old[207]). This recent origin of these gypsum sand dunes suggests that species exhibiting lighter-colored variations have evolved in a relatively short time frame. The three lizard species previously mentioned have been found to display variable social signal coloration in coexistence with their ecotonal variants.[210] Not only have the three species convergently evolved their lighter variants due to the selection pressures from the environment, they have also evolved ecomorphological differences: morphology, behavior (in is case, escape behavior), and performance (in this case, sprint speed) collectively.[209] Roches' work found surprising results in the escape behavior of H. maculata and S. undulatus. When dark morphs were placed on white sands, their startle response was significantly diminished. This result could be due to varying factors relating to sand temperature or visual acuity; however, regardless of the cause, "…failure of mismatched lizards to sprint could be maladaptive when faced with a predator".[209]
Evidence from speciation[edit]
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. Biologists research species using different theoretical frameworks for what constitutes a species (see species problem and species complex) and there exists debate with regard to delineation.[211] Nevertheless, much of the current research suggests that, "...speciation is a process of emerging genealogical distinctness, rather than a discontinuity affecting all genes simultaneously"[212] and, in allopatry (the most common form of speciation), "reproductive isolation is a byproduct of evolutionary change in isolated populations, and thus can be considered an evolutionary accident".[213] Speciation occurs as the result of the latter (allopatry); however, a variety of differing agents have been documented and are often defined and classified in various forms (e.g. peripatric, parapatric, sympatric, polyploidization, hybridization, etc.). Instances of speciation have been observed in both nature and the laboratory. A.-B Florin and A. Ödeen note that, "strong laboratory evidence for allopatric speciation is lacking..."; however, contrary to laboratory studies (focused specifically on models of allopatric speciation), "speciation most definitely occurs; [and] the vast amount of evidence from nature makes it unreasonable to argue otherwise".[214] Coyne and Orr compiled a list of 19 laboratory experiments on Drosophila presenting examples of allopatric speciation by divergent selection concluding that, "reproductive isolation in allopatry can evolve as a byproduct of divergent selection".[215]
Research documenting speciation is abundant. Biologists have documented numerous examples of speciation in nature—with evolution having produced far more species than any observer would consider necessary. For example, there are well over 350,000 described species of beetles.[216] Examples of speciation come from the observations of island biogeography and the process of adaptive radiation, both explained previously. Evidence of common descent can also be found through paleontological studies of speciation within geologic strata. The examples described below represent different modes of speciation and provide strong evidence for common descent. It is important to acknowledge that not all speciation research directly observes divergence from "start-to-finish". This is by virtue of research delimitation and definition ambiguity, and occasionally leads research towards historical reconstructions. In light of this, examples abound, and the following are by no means exhaustive—comprising only a small fraction of the instances observed. Once again, take note of the established fact that, "...natural selection is a ubiquitous part of speciation...",[166] and is the primary driver of speciation,[167] so; hereinafter, examples of speciation will often interdepend and correspond with selection.
Fossils[edit]
Limitations exist within the fossil record when considering the concept of what constitutes a species. Paleontologists largely rely on a different framework: the morphological species concept.[217] Due to the absence of information such as reproductive behavior or genetic material in fossils, paleontologists distinguish species by their phenotypic differences.[217] Extensive investigation of the fossil record has led to numerous theories concerning speciation (in the context of paleontology) with many of the studies suggesting that stasis, punctuation, and lineage branching are common. In 1995, D. H. Erwin, et al. published a major work—New Approaches to Speciation in the Fossil Record—which compiled 58 studies of fossil speciation (between 1972 and 1995) finding most of the examples suggesting stasis (involving anagenesis or punctuation) and 16 studies suggesting speciation.[217] Despite stasis appearing to be the predominant conclusion at first glance, this particular meta-study investigated deeper, concluding that, "...no single pattern appears dominant..." with "...the preponderance of studies illustrating both stasis and gradualism in the history of a single lineage".[218] Many of the studies conducted utilize seafloor sediments that can provide a significant amount of data concerning planktonic microfossils.[217] The succession of fossils in stratigraphy can be used to determine evolutionary trends among fossil organisms. In addition, incidences of speciation can be interpreted from the data and numerous studies have been conducted documenting both morphological evolution and speciation.
Globorotalia[edit]
Extensive research on the planktonic foraminifer Globorotalia truncatulinoides has provided insight into paleobiogeographical and paleoenvironmental studies alongside the relationship between the environment and evolution. In an extensive study of the paleobiogeography of G. truncatulinoides, researchers found evidence that suggested the formation of a new species (via the sympatric speciation framework). Cores taken of the sediment containing the three species G. crassaformis, G. tosaensis, and G. truncatulinoides found that before 2.7 Ma, only G. crassaformis and G. tosaensis existed. A speciation event occurred at that time, whereby intermediate forms existed for quite some time. Eventually G. tosaensis disappears from the record (suggesting extinction) but exists as an intermediate between the extant G. crassaformis and G. truncatulinoides. This record of the fossils also matched the already existing phylogeny constructed by morphological characters of the three species.[219] See figure 6a.
Radiolaria[edit]
In a large study of five species of radiolarians (Calocycletta caepa, Pterocanium prismatium, Pseudoculous vema, Eucyrtidium calvertense, and Eucyrtidium matuyamai), the researchers documented considerable evolutionary change in each lineage. Alongside this, trends with the closely related species E. calvertense and E. matuyamai showed that about 1.9 Mya E. calvertense invaded a new region of the Pacific, becoming isolated from the main population. The stratigraphy of this species clearly shows that this isolated population evolved into E. Matuyamai. It then reinvaded the region of the still-existing and static E. calvertense population whereby a sudden decrease in body size occurred. Eventually the invader E. matuyamai disappeared from the stratum (presumably due to extinction) coinciding with a desistance of size reduction of the E. calvertense population. From that point on, the change in size leveled to a constant. The authors suggest competition-induced character displacement.[220][221]
Rhizosolenia[edit]
Researchers conducted measurements on 5,000 Rhizosolenia (a planktonic diatom) specimens from eight sedimentary cores in the Pacific Ocean. The core samples spanned two million years and were chronologized using sedimentary magnetic field reversal measurements. All the core samples yielded a similar pattern of divergence: with a single lineage (R. bergonii) occurring before 3.1 Mya and two morphologically distinct lineages (daughter species: R. praebergonii) appearing after. The parameters used to measure the samples were consistent throughout each core.[222] An additional study of the daughter species R. praebergonii found that, after the divergence, it invaded the Indian Ocean.[217][223]
Turborotalia[edit]
A recent study was conducted involving the planktonic foraminifer Turborotalia. The authors extracted "51 stratigraphically ordered samples from a site within the oceanographically stable tropical North Pacific gyre". Two hundred individual species were examined using ten specific morphological traits (size, compression index, chamber aspect ratio, chamber inflation, aperture aspect ratio, test height, test expansion, umbilical angle, coiling direction, and the number of chambers in the final whorl). Utilizing multivariate statistical clustering methods, the study found that the species continued to evolve non-directionally within the Eocene from 45 Ma to about 36 Ma. However, from 36 Ma to approximately 34 Ma, the stratigraphic layers showed two distinct clusters with significantly defining characteristics distinguishing one another from a single species. The authors concluded that speciation must have occurred and that the two new species were descended from the prior species.[224]
Vertebrates[edit]
There exists evidence for vertebrate speciation despite limitations imposed by the fossil record. Studies have been conducted documenting similar patterns seen in marine invertebrates.[217] For example, extensive research documenting rates of morphological change, evolutionary trends, and speciation patterns in small mammals has significantly contributed to the scientific literature.[225]
A study of four mammalian genera: Hyopsodus, Pelycodus, Haplomylus (three from the Eocene), and Plesiadapis (from the Paleocene) found that—through a large number of stratigraphic layers and specimen sampling—each group exhibited, "gradual phyletic evolution, overall size increase, iterative evolution of small species, and character divergence following the origin of each new lineage".[226] The authors of this study concluded that speciation was discernible. In another study concerning morphological trends and rates of evolution found that the European arvicolid rodent radiated into 52 distinct lineages over a time frame of 5 million years while documenting examples of phyletic gradualism, punctuation, and stasis.[227]
Invertebrates[edit]
Drosophila melanogaster[edit]

William R. Rice and George W. Salt found experimental evidence of sympatric speciation in the common fruit fly. They collected a population of Drosophila melanogaster from Davis, California and placed the pupae into a habitat maze. Newborn flies had to investigate the maze to find food. The flies had three choices to take in finding food. Light and dark (phototaxis), up and down (geotaxis), and the scent of acetaldehyde and the scent of ethanol (chemotaxis) were the three options. This eventually divided the flies into 42 spatio-temporal habitats. They then cultured two strains that chose opposite habitats. One of the strains emerged early, immediately flying upward in the dark attracted to the acetaldehyde. The other strain emerged late and immediately flew downward, attracted to light and ethanol. Pupae from the two strains were then placed together in the maze and allowed to mate at the food site. They then were collected. A selective penalty was imposed on the female flies that switched habitats. This entailed that none of their gametes would pass on to the next generation. After 25 generations of this mating test, it showed reproductive isolation between the two strains. They repeated the experiment again without creating the penalty against habitat switching and the result was the same; reproductive isolation was produced.[228][229][230]
Gall wasps[edit]
A study of the gall-forming wasp species Belonocnema treatae found that populations inhabiting different host plants (Quercus geminata and Q. virginiana) exhibited different body size and gall morphology alongside a strong expression of sexual isolation. The study hypothesized that B. treatae populations inhabiting different host plants would show evidence of divergent selection promoting speciation. The researchers sampled gall wasp species and oak tree localities, measured body size (right hand tibia of each wasp), and counted gall chamber numbers. In addition to measurements, they conducted mating assays and statistical analyses. Genetic analysis was also conducted on two mtDNA sites (416 base pairs from cytochrome C and 593 base pairs from cytochrome oxidase ) to "control for the confounding effects of time since divergence among allopatric populations".[231]
In an additional study, the researchers studied two gall wasp species B. treatae and Disholcaspis quercusvirens and found strong morphological and behavioral variation among host-associated populations. This study further confounded prerequisites to speciation.[232]
Hawthorn fly[edit]
One example of evolution at work is the case of the hawthorn fly, Rhagoletis pomonella, also known as the apple maggot fly, which appears to be undergoing sympatric speciation.[233] Different populations of hawthorn fly feed on different fruits. A distinct population emerged in North America in the 19th century some time after apples, a non-native species, were introduced. This apple-feeding population normally feeds only on apples and not on the historically preferred fruit of hawthorns. The current hawthorn feeding population does not normally feed on apples. Some evidence, such as the fact that six out of thirteen allozyme loci are different, that hawthorn flies mature later in the season and take longer to mature than apple flies; and that there is little evidence of interbreeding (researchers have documented a 4–6% hybridization rate) suggests that speciation is occurring.[234][235][236][237][238]
London Underground mosquito[edit]
The London Underground mosquito is a species of mosquito in the genus Culex found in the London Underground. It evolved from the overground species Culex pipiens. This mosquito, although first discovered in the London Underground system, has been found in underground systems around the world. It is suggested that it may have adapted to human-made underground systems since the last century from local above-ground Culex pipiens,[239] although more recent evidence suggests that it is a southern mosquito variety related to Culex pipiens that has adapted to the warm underground spaces of northern cities.[240]
The two species have very different behaviours,[241] are extremely difficult to mate,[239] and with different allele frequency, consistent with genetic drift during a founder event.[242] More specifically, this mosquito, Culex pipiens molestus, breeds all-year round, is cold intolerant, and bites rats, mice, and humans, in contrast to the above ground species Culex pipiens that is cold tolerant, hibernates in the winter, and bites only birds. When the two varieties were cross-bred the eggs were infertile suggesting reproductive isolation.[239][241]
The genetic data indicates that the molestus form in the London Underground mosquito appears to have a common ancestry, rather than the population at each station being related to the nearest aboveground population (i.e. the pipiens form). Byrne and Nichols' working hypothesis was that adaptation to the underground environment had occurred locally in London only once. These widely separated populations are distinguished by very minor genetic differences, which suggest that the molestus form developed: a single mtDNA difference shared among the underground populations of ten Russian cities;[243] a single fixed microsatellite difference in populations spanning Europe, Japan, Australia, the middle East and Atlantic islands.[240]
Snapping shrimp and the isthmus of Panama[edit]
Debate exists determining when the isthmus of Panama closed. Much of the evidence supports a closure approximately 2.7 to 3.5 mya using "...multiple lines of evidence and independent surveys".[244] However, a recent study suggests an earlier, transient bridge existed 13 to 15 mya.[245] Regardless of the timing of the isthmus closer, biologists can study the species on the Pacific and Caribbean sides in, what has been called, "one of the greatest natural experiments in evolution."[244] Studies of snapping shrimp in the genus Alpheus have provided direct evidence of allopatric speciation events,[246] and contributed to the literature concerning rates of molecular evolution.[247] Phylogenetic reconstructions using "multilocus datasets and coalescent-based analytical methods" support the relationships of the species in the group[244] and molecular clock techniques support the separation of 15 pairs of Alpheus species between 3 and 15 million years ago.[247]
Plants[edit]
The botanist Verne Grant pioneered the field of plant speciation with his research and major publications on the topic.[248] As stated before, many biologists rely on the biological species concept, with some modern researchers utilizing the phylogenetic species concept. Debate exists in the field concerning which framework should be applied in the research.[248] Regardless, reproductive isolation is the primary role in the process of speciation and has been studied extensively by biologists in their respective disciplines.
Both hybridization and polyploidy have also been found to be major contributors to plant speciation.[249] With the advent of molecular markers, "hybridization [is] considerably more frequent than previously believed".[248] In addition to these two modes leading to speciation, pollinator preference and isolation, chromosomal rearrangements, and divergent natural selection have become critical to the speciation of plants. Furthermore, recent research suggests that sexual selection, epigenetic drivers, and the creation of incompatible allele combinations caused by balancing selection also contribute to the formation of new species.[249] Instances of these modes have been researched in both the laboratory and in nature. Studies have also suggested that, due to "the sessile nature of plants... [it increases] the relative importance of ecological speciation..."[250]
Hybridization between two different species sometimes leads to a distinct phenotype. This phenotype can also be fitter than the parental lineage and as such, natural selection may then favor these individuals. Eventually, if reproductive isolation is achieved, it may lead to a separate species. However, reproductive isolation between hybrids and their parents is particularly difficult to achieve and thus hybrid speciation is considered a rare event. However, hybridization resulting in reproductive isolation is considered an important means of speciation in plants,[251] since polyploidy (having more than two copies of each chromosome) is tolerated in plants more readily than in animals.[252][253]
Polyploidy is important in hybrids as it allows reproduction, with the two different sets of chromosomes each being able to pair with an identical partner during meiosis.[254] Polyploids also have more genetic diversity, which allows them to avoid inbreeding depression in small populations.[255] Hybridization without change in chromosome number is called homoploid hybrid speciation. It is considered very rare but has been shown in Heliconius butterflies[256] and sunflowers. Polyploid speciation, which involves changes in chromosome number, is a more common phenomenon, especially in plant species.
Polyploidy is a mechanism that has caused many rapid speciation events in sympatry because offspring of, for example, tetraploid x diploid matings often result in triploid sterile progeny.[257] Not all polyploids are reproductively isolated from their parental plants, and gene flow may still occur for example through triploid hybrid x diploid matings that produce tetraploids, or matings between meiotically unreduced gametes from diploids and gametes from tetraploids. It has been suggested that many of the existing plant and most animal species have undergone an event of polyploidization in their evolutionary history.[254][258] Reproduction of successful polyploid species is sometimes asexual, by parthenogenesis or apomixis, as for unknown reasons many asexual organisms are polyploid. Rare instances of polyploid mammals are known, but most often result in prenatal death.
Researchers consider reproductive isolation as key to speciation.[259] A major aspect of speciation research is to determine the nature of the barriers that inhibit reproduction. Botanists often consider the zoological classifications of prezygotic and postzygotic barriers as inadequate.[259] The examples provided below give insight into the process of speciation.
Mimulus peregrinus[edit]
The creation of a new allopolyploid species of monkeyflower (Mimulus peregrinus) was observed on the banks of the Shortcleuch Water—a river in Leadhills, South Lanarkshire, Scotland. Parented from the cross of the two species Mimulus guttatus (containing 14 pairs of chromosomes) and Mimulus luteus (containing 30-31 pairs from a chromosome duplication), M. peregrinus has six copies of its chromosomes (caused by the duplication of the sterile hybrid triploid). Due to the nature of these species, they have the ability to self-fertilize. Because of its number of chromosomes it is not able to pair with M. guttatus, M. luteus, or their sterile triploid offspring. M. peregrinus will either die, producing no offspring, or reproduce with itself effectively leading to a new species.[260][261]
Raphanobrassica[edit]
Raphanobrassica includes all intergeneric hybrids between the genera Raphanus (radish) and Brassica (cabbages, etc.).[262][263] The Raphanobrassica is an allopolyploid cross between the radish (Raphanus sativus) and cabbage (Brassica oleracea). Plants of this parentage are now known as radicole. Two other fertile forms of Raphanobrassica are known. Raparadish, an allopolyploid hybrid between Raphanus sativus and Brassica rapa is grown as a fodder crop. "Raphanofortii" is the allopolyploid hybrid between Brassica tournefortii and Raphanus caudatus. The Raphanobrassica is a fascinating plant, because (in spite of its hybrid nature), it is not sterile. This has led some botanists to propose that the accidental hybridization of a flower by pollen of another species in nature could be a mechanism of speciation common in higher plants.
Senecio (groundsel)[edit]
The Welsh groundsel is an allopolyploid, a plant that contains sets of chromosomes originating from two different species. Its ancestor was Senecio × baxteri, an infertile hybrid that can arise spontaneously when the closely related groundsel (Senecio vulgaris) and Oxford ragwort (Senecio squalidus) grow alongside each other. Sometime in the early 20th century, an accidental doubling of the number of chromosomes in an S. × baxteri plant led to the formation of a new fertile species.[264][265]
The York groundsel (Senecio eboracensis) is a hybrid species of the self-incompatible Senecio squalidus (also known as Oxford ragwort) and the self-compatible Senecio vulgaris (also known as common groundsel). Like S. vulgaris, S. eboracensis is self-compatible; however, it shows little or no natural crossing with its parent species, and is therefore reproductively isolated, indicating that strong breed barriers exist between this new hybrid and its parents. It resulted from a backcrossing of the F1 hybrid of its parents to S. vulgaris. S. vulgaris is native to Britain, while S. squalidus was introduced from Sicily in the early 18th century; therefore, S. eboracensis has speciated from those two species within the last 300 years.
Other hybrids descended from the same two parents are known. Some are infertile, such as S. x baxteri. Other fertile hybrids are also known, including S. vulgaris var. hibernicus, now common in Britain, and the allohexaploid S. cambrensis, which according to molecular evidence probably originated independently at least three times in different locations. Morphological and genetic evidence support the status of S. eboracensis as separate from other known hybrids.[266]
Thale cress[edit]

Kirsten Bomblies et al. from the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology discovered two genes in the thale cress plant, Arabidopsis thaliana. When both genes are inherited by an individual, it ignites a reaction in the hybrid plant that turns its own immune system against it. In the parents, the genes were not detrimental, but they evolved separately to react defectively when combined.[267] To test this, Bomblies crossed 280 genetically different strains of Arabidopsis in 861 distinct ways and found that 2 percent of the resulting hybrids were necrotic. Along with allocating the same indicators, the 20 plants also shared a comparable collection of genetic activity in a group of 1,080 genes. In almost all of the cases, Bomblies discovered that only two genes were required to cause the autoimmune response. Bomblies looked at one hybrid in detail and found that one of the two genes belonged to the NB-LRR class, a common group of disease resistance genes involved in recognizing new infections. When Bomblies removed the problematic gene, the hybrids developed normally.[267] Over successive generations, these incompatibilities could create divisions between different plant strains, reducing their chances of successful mating and turning distinct strains into separate species.[268]
Tragopogon (salsify)[edit]

Tragopogon is one example where hybrid speciation has been observed. In the early 20th century, humans introduced three species of salsify into North America. These species, the western salsify (Tragopogon dubius), the meadow salsify (Tragopogon pratensis), and the oyster plant (Tragopogon porrifolius), are now common weeds in urban wastelands. In the 1950s, botanists found two new species in the regions of Idaho and Washington, where the three already known species overlapped. One new species, Tragopogon miscellus, is a tetraploid hybrid of T. dubius and T. pratensis. The other new species, Tragopogon mirus, is also an allopolyploid, but its ancestors were T. dubius and T. porrifolius. These new species are usually referred to as "the Ownbey hybrids" after the botanist who first described them. The T. mirus population grows mainly by reproduction of its own members, but additional episodes of hybridization continue to add to the T. mirus population.[269]
T. dubius and T. pratensis mated in Europe but were never able to hybridize. A study published in March 2011 found that when these two plants were introduced to North America in the 1920s, they mated and doubled the number of chromosomes in there hybrid Tragopogon miscellus allowing for a "reset" of its genes, which in turn, allows for greater genetic variation. Professor Doug Soltis of the University of Florida said, "We caught evolution in the act…New and diverse patterns of gene expression may allow the new species to rapidly adapt in new environments".[270][271]
Vertebrates[edit]
Blackcap[edit]
The bird species, Sylvia atricapilla, commonly referred to as blackcaps, lives in Germany and flies southwest to Spain while a smaller group flies northwest to Great Britain during the winter. Gregor Rolshausen from the University of Freiburg found that the genetic separation of the two populations is already in progress. The differences found have arisen in about 30 generations. With DNA sequencing, the individuals can be assigned to a correct group with an 85% accuracy. Stuart Bearhop from the University of Exeter reported that birds wintering in England tend to mate only among themselves, and not usually with those wintering in the Mediterranean.[272] It is still inference to say that the populations will become two different species, but researchers expect it due to the continued genetic and geographic separation.[273]
Mollies[edit]
The shortfin molly (Poecilia mexicana) is a small fish that lives in the Sulfur Caves of Mexico. Years of study on the species have found that two distinct populations of mollies—the dark interior fish and the bright surface water fish—are becoming more genetically divergent.[274] The populations have no obvious barrier separating the two; however, it was found that the mollies are hunted by a large water bug (Belostoma spp). Tobler collected the bug and both types of mollies, placed them in large plastic bottles, and put them back in the cave. After a day, it was found that, in the light, the cave-adapted fish endured the most damage, with four out of every five stab-wounds from the water bugs sharp mouthparts. In the dark, the situation was the opposite. The mollies' senses can detect a predator's threat in their own habitats, but not in the other ones. Moving from one habitat to the other significantly increases the risk of dying. Tobler plans on further experiments, but believes that it is a good example of the rise of a new species.[275]
Polar bear[edit]
Natural selection, geographic isolation, and speciation in progress are illustrated by the relationship between the polar bear (Ursus maritimus) and the brown bear (Ursus arctos). Considered separate species throughout their ranges;[276] however, it has been documented that they possess the capability to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. This introgressive hybridization has occurred both in the wild and in captivity and has been documented[277] and verified with DNA testing.[278] The oldest known fossil evidence of polar bears dates around 130,000 to 110,000 years ago;[279] however, molecular data has revealed varying estimates of divergence time. Mitochondrial DNA analysis has given an estimate of 150,000 years ago[279] while nuclear genome analysis has shown an approximate divergence of 603,000 years ago.[280] Recent research using the complete genomes (rather than mtDNA or partial nuclear genomes) establishes the divergence of polar and brown bears between 479 and 343 thousand years ago.[281] Despite the differences in divergence rates, molecular research suggests the sister species have undergone a highly complex process of speciation and admixture between the two.[282]
The polar bear has acquired anatomical and physiological differences from the brown bear that allow it to comfortably survive in conditions that the brown bear likely could not. Notable examples include the ability to swim sixty miles or more at a time in freezing waters, fur that blends with the snow, and to stay warm in the arctic environment, an elongated neck that makes it easier to keep their heads above water while swimming, and oversized and heavy-matted webbed feet that act as paddles when swimming. It has also evolved small papillae and vacuole-like suction cups on the soles to make them less likely to slip on the ice, alongside smaller ears for a reduction of heat loss, eyelids that act like sunglasses, accommodations for their all-meat diet, a large stomach capacity to enable opportunistic feeding, and the ability to fast for up to nine months while recycling their urea.[283][284]
Evidence from coloration[edit]

Animal coloration provided important early evidence for evolution by natural selection, at a time when little direct evidence was available. Three major functions of coloration were discovered in the second half of the 19th century, and subsequently used as evidence of selection: camouflage (protective coloration); mimicry, both Batesian and Müllerian; and aposematism. After the circumstantial evidence provided by Darwin in On the Origin of Species, and given the absence of mechanisms for genetic variation or heredity at that time, naturalists including Darwin's contemporaries, Henry Walter Bates and Fritz Müller sought evidence from what they could observe in the field.[286]
Mimicry and aposematism[edit]
Bates and Müller described forms of mimicry that now carry their names, based on their observations of tropical butterflies. These highly specific patterns of coloration are readily explained by natural selection, since predators such as birds which hunt by sight will more often catch and kill insects that are less good mimics of distasteful models than those that are better mimics; but the patterns are otherwise hard to explain.[287] Darwinists such as Alfred Russel Wallace and Edward Bagnall Poulton, and in the 20th century Hugh Cott and Bernard Kettlewell, sought evidence that natural selection was taking place.[288][289] The efficacy of mimicry in butterflies was demonstrated in controlled experiments by Jane Van Zandt Brower in 1958.[290][291][292]
Camouflage[edit]
In 1889, Wallace noted that snow camouflage, especially plumage and pelage that changed with the seasons, suggested an obvious explanation as an adaptation for concealment.[293][285] Poulton's 1890 book, The Colours of Animals, written during Darwinism's lowest ebb, used all the forms of coloration to argue the case for natural selection.[294] Cott described many kinds of camouflage, mimicry and warning coloration in his 1940 book Adaptive Coloration in Animals, and in particular his drawings of coincident disruptive coloration in frogs convinced other biologists that these deceptive markings were products of natural selection.[288] Kettlewell experimented on peppered moth evolution, showing that the species had adapted as pollution changed the environment; this provided compelling evidence of Darwinian evolution.[289]
Evidence from behavior[edit]
Some primitive reflexes are critical for the survival of neonates. There is evidence confirming that closely related species share more similar primitive reflexes, such as the type of fur-grasping in primates and their relationship to manual dexterity. The exact selection pressures for their development are not fully determined and some reflexes are understood to have evolved multiple times independently (convergent evolution).[295]
Evidence from mathematical modeling and simulation[edit]
Computer science allows the iteration of self-changing complex systems to be studied, allowing a mathematical understanding of the nature of the processes behind evolution; providing evidence for the hidden causes of known evolutionary events. The evolution of specific cellular mechanisms like spliceosomes that can turn the cell's genome into a vast workshop of billions of interchangeable parts that can create tools that create us can be studied for the first time in an exact way.
"It has taken more than five decades, but the electronic computer is now powerful enough to simulate evolution",[296] assisting bioinformatics in its attempt to solve biological problems.
Computational evolutionary biology has enabled researchers to trace the evolution of a large number of organisms by measuring changes in their DNA, rather than through physical taxonomy or physiological observations alone. It has compared entire genomes permitting the study of more complex evolutionary events, such as gene duplication, horizontal gene transfer, and the prediction of factors important in speciation. It has also helped build complex computational models of populations to predict the outcome of the system over time and track and share information on an increasingly large number of species and organisms.
Future endeavors are to reconstruct a now more complex tree of life.
Christoph Adami, a professor at the Keck Graduate Institute made this point in Evolution of biological complexity:
- To make a case for or against a trend in the evolution of complexity in biological evolution, complexity must be both rigorously defined and measurable. A recent information-theoretic (but intuitively evident) definition identifies genomic complexity with the amount of information a sequence stores about its environment. We investigate the evolution of genomic complexity in populations of digital organisms and monitor in detail the evolutionary transitions that increase complexity. We show that, because natural selection forces genomes to behave as a natural "Maxwell Demon", within a fixed environment, genomic complexity is forced to increase.[297]
David J. Earl and Michael W. Deem—professors at Rice University made this point in Evolvability is a selectable trait:
- Not only has life evolved, but life has evolved to evolve. That is, correlations within protein structure have evolved, and mechanisms to manipulate these correlations have evolved in tandem. The rates at which the various events within the hierarchy of evolutionary moves occur are not random or arbitrary but are selected by Darwinian evolution. Sensibly, rapid or extreme environmental change leads to selection for greater evolvability. This selection is not forbidden by causality and is strongest on the largest-scale moves within the mutational hierarchy. Many observations within evolutionary biology, heretofore considered evolutionary happenstance or accidents, are explained by selection for evolvability. For example, the vertebrate immune system shows that the variable environment of antigens has provided selective pressure for the use of adaptable codons and low-fidelity polymerases during somatic hypermutation. A similar driving force for biased codon usage as a result of productively high mutation rates is observed in the hemagglutinin protein of influenza A.[298]
"Computer simulations of the evolution of linear sequences have demonstrated the importance of recombination of blocks of sequence rather than point mutagenesis alone. Repeated cycles of point mutagenesis, recombination, and selection should allow in vitro molecular evolution of complex sequences, such as proteins."[299] Evolutionary molecular engineering, also called directed evolution or in vitro molecular evolution involves the iterated cycle of mutation, multiplication with recombination, and selection of the fittest of individual molecules (proteins, DNA, and RNA). Natural evolution can be relived showing us possible paths from catalytic cycles based on proteins to based on RNA to based on DNA.[299][300][301][302]
The Avida artificial life software platform has been used to explore common descent and natural selection.[303][304] It has been used to demonstrate that natural selection can favor altruism, something that had been predicted but is difficult to test empirically. At the higher replication rates allowed by the platform it becomes observable.[305]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Mount, D.M. (2004). Bioinformatics: Sequence and Genome Analysis (2nd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY. ISBN 978-0-87969-608-5.
- ^ Penny, David; Foulds, L. R.; Hendy, M. D. (1982). "Testing the theory of evolution by comparing phylogenetic trees constructed from five different protein sequences". Nature. 297 (5863): 197–200. Bibcode:1982Natur.297..197P. doi:10.1038/297197a0. PMID 7078635. S2CID 4270111.
- ^ "Eukaryotes". www.tolweb.org. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- ^ Max, Edward (5 May 2003). "Plagiarized Errors and Molecular Genetics". The Talk Origins Archive. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^ Futuyma, Douglas J. (1998). Evolutionary Biology (3rd ed.). Sinauer Associates. pp. 108–110. ISBN 978-0-87893-189-7.
- ^ Haszprunar (1995). "The mollusca: Coelomate turbellarians or mesenchymate annelids?". In Taylor (ed.). Origin and evolutionary radiation of the Mollusca : centenary symposium of the Malacological Society of London. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-854980-2.
- ^ Kozmik, Z.; Daube, M.; Frei, E.; Norman, B.; Kos, L.; Dishaw, L.J.; Noll, M.; Piatigorsky, J. (2003). "Role of Pax genes in eye evolution: A cnidarian PaxB gene uniting Pax2 and Pax6 functions" (PDF). Developmental Cell. 5 (5): 773–785. doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00325-3. PMID 14602077.
- ^ Land, M.F. and Nilsson, D.-E., Animal Eyes, Oxford University Press, Oxford (2002) ISBN 0-19-850968-5.
- ^ De Robertis, Eddy M.; Oliver, Guillermo; Wright, Christopher V. E. (July 1990). "Homeobox Genes and the Vertebrate Body Plan". Scientific American. 263 (1): 46–53. Bibcode:1990SciAm.263a..46D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0790-46. JSTOR 24996862. PMID 1973846.
- ^ Chen, F.C.; Li, W.H. (2001). "Genomic Divergences between Humans and Other Hominoids and the Effective Population Size of the Common Ancestor of Humans and Chimpanzees". American Journal of Human Genetics. 68 (2): 444–56. doi:10.1086/318206. PMC 1235277. PMID 11170892.
- ^ Cooper, G.M.; Brudno, M.; Green, E.D.; Batzoglou, S.; Sidow, A. (2003). "Quantitative Estimates of Sequence Divergence for Comparative Analyses of Mammalian Genomes". Genome Res. 13 (5): 813–20. doi:10.1101/gr.1064503. PMC 430923. PMID 12727901.
- ^ The picture labeled "Human Chromosome 2 and its analogs in the apes" in the article Comparison of the Human and Great Ape Chromosomes as Evidence for Common Ancestry Archived 23 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine is literally a picture of a link in humans that links two separate chromosomes in the nonhuman apes creating a single chromosome in humans. Also, while the term originally referred to fossil evidence, this too is a trace from the past corresponding to some living beings that, when alive, physically embodied this link.
- ^ The New York Times report Still Evolving, Human Genes Tell New Story, based on A Map of Recent Positive Selection in the Human Genome, states the International HapMap Project is "providing the strongest evidence yet that humans are still evolving" and details some of that evidence.
- ^ Woese, Carl R.; Fox, G. E. (November 1977). "Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 74 (11): 5088–90. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74.5088W. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. PMC 432104. PMID 270744.
- ^ Woese, Carl R.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M. L. (June 1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (12): 4576–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.4576W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. PMC 54159. PMID 2112744.
- ^ Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter (March 2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-0-8153-3218-3.
- ^ "Converging Evidence for Evolution." Archived 1 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine Phylointelligence: Evolution for Everyone. 26 November 2010.
- ^ Petrov, D.A.; Hartl, D.L. (2000). "Pseudogene evolution and natural selection for a compact genome". The Journal of Heredity. 91 (3): 221–7. doi:10.1093/jhered/91.3.221. PMID 10833048.
- ^ a b Xiao-Jie, Lu; Ai-Mei, Gao; Li-Juan, Ji; Jiang, Xu (1 January 2015). "Pseudogene in cancer: real functions and promising signature". Journal of Medical Genetics. 52 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102785. ISSN 0022-2593. PMID 25391452.
- ^ Vanin, E F (1985). "Processed Pseudogenes: Characteristics and Evolution". Annual Review of Genetics. 19 (1): 253–272. doi:10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001345. ISSN 0066-4197. PMID 3909943.
- ^ Gerstein, Mark (2006). "Pseudogenes in the ENCODE Regions: Consensus Annotation, Analysis of Transcription and Evolution" (PDF). Genome Research. 17 (6): 839–51. doi:10.1101/gr.5586307. PMC 1891343. PMID 17568002. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- ^ "What is Junk DNA?". News-Medical.net. 7 May 2010. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- ^ Okamoto, N.; Inouye, I. (2005). "A secondary symbiosis in progress". Science. 310 (5746): 287. doi:10.1126/science.1116125. PMID 16224014. S2CID 22081618.
- ^ Okamoto, N.; Inouye, I. (2006). "Hatena arenicola gen. et sp. nov., a katablepharid undergoing probable plastid acquisition". Protist. 157 (4): 401–19. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2006.05.011. PMID 16891155.
- ^ MacAndrew, Alec. Human Chromosome 2 is a fusion of two ancestral chromosomes. Accessed 18 May 2006.
- ^ Evidence of Common Ancestry: Human Chromosome 2 (video) 2007
- ^ Yunis, J.J.; Prakash, O. (1982). "The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy". Science. 215 (4539): 1525–1530. Bibcode:1982Sci...215.1525Y. doi:10.1126/science.7063861. PMID 7063861.
- ^ Human and Ape Chromosomes Archived 23 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine; accessed 8 September 2007.
- ^ Avarello, Rosamaria; Pedicini, A; Caiulo, A; Zuffardi, O; Fraccaro, M (1992). "Evidence for an ancestral alphoid domain on the long arm of human chromosome 2". Human Genetics. 89 (2): 247–9. doi:10.1007/BF00217134. PMID 1587535. S2CID 1441285.
- ^ a b Ijdo, J. W.; Baldini, A; Ward, DC; Reeders, ST; Wells, RA (1991). "Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere-telomere fusion". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 88 (20): 9051–5. Bibcode:1991PNAS...88.9051I. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.20.9051. PMC 52649. PMID 1924367.
- ^ a b Amino acid sequences in cytochrome c proteins from different species Archived 28 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine, adapted from Strahler, Arthur; Science and Earth History, 1997. page 348.
- ^ Lurquin, P.F.; Stone, L. (2006). Genes, Culture, and Human Evolution: A Synthesis. Blackwell Publishing, Incorporated. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-4051-5089-7.
- ^ a b Theobald, Douglas (2004). "29+ Evidences for Macroevolution; Protein functional redundancy". The Talk Origins Archive.
- ^ Castresana, J. (2001). "Cytochrome b Phylogeny and the Taxonomy of Great Apes and Mammals". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 18 (4): 465–471. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003825. PMID 11264397.
- ^ Van Der Kuyl, A.C.; Dekker, J.T.; Goudsmit, J. (1999). "Discovery of a New Endogenous Type C Retrovirus (FcEV) in Cats: Evidence for RD-114 Being an FcEVGag-Pol/Baboon Endogenous Virus BaEVEnv Recombinant". Journal of Virology. 73 (10): 7994–8002. doi:10.1128/JVI.73.10.7994-8002.1999. PMC 112814. PMID 10482547.
- ^ Sverdlov, E.D. (February 2000). "Retroviruses and primate evolution". BioEssays. 22 (2): 161–71. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(200002)22:2<161::AID-BIES7>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 10655035.
- ^ Belshaw, R.; Pereira, V.; Katzourakis, A.; et al. (April 2004). "Long-term reinfection of the human genome by endogenous retroviruses". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (14): 4894–9. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.4894B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307800101. PMC 387345. PMID 15044706.
- ^ Bonner, T.I.; O'Connell, C.; Cohen, M. (August 1982). "Cloned endogenous retroviral sequences from human DNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 79 (15): 4709–13. Bibcode:1982PNAS...79.4709B. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.15.4709. PMC 346746. PMID 6181510.
- ^ Johnson, Welkin E.; Coffin, John M. (31 August 1999). "Constructing primate phylogenies from ancient retrovirus sequences". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 96 (18): 10254–10260. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9610254J. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.18.10254. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 17875. PMID 10468595.
- ^ Pallen, Mark (2009). Rough Guide to Evolution. Rough Guides. pp. 200–206. ISBN 978-1-85828-946-5.
- ^ Tanaka, G.; Hou, X.; Ma, X.; Edgecombe, G.D.; Strausfeld, N.J. (October 2013). "Chelicerate neural ground pattern in a Cambrian great appendage arthropod". Nature. 502 (7471): 364–367. Bibcode:2013Natur.502..364T. doi:10.1038/nature12520. PMID 24132294. S2CID 4456458.
- ^ Andrews, Roy Chapman (3 June 1921). "A Remarkable Case of External Hind Limbs in a Humpback Whale" (PDF). American Museum Novitates. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- ^ a b Hall, Brian K. (1995), "Atavisms and atavistic mutations", Nature Genetics, 10 (2): 126–127, doi:10.1038/ng0695-126, PMID 7663504, S2CID 27868367
- ^ a b c d e f g h i hall, Brian K. (1984), "Developmental mechanisms underlying the atavisms", Biological Reviews, 59 (1): 89–124, doi:10.1111/j.1469-185x.1984.tb00402.x, PMID 6367843, S2CID 29258934
- ^ Lambert, Katie. (29 October 2007) HowStuffWorks "How Atavisms Work". Animals.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved on 2011-12-06.
- ^ a b Tomić, Nenad; et al. (2011), "Atavisms: Medical, Genetic, and Evolutionary Implications", Perspectives in Biology and Medicine, 54 (3): 332–353, doi:10.1353/pbm.2011.0034, PMID 21857125, S2CID 40851098
- ^ Raynaud, A. (1977), Somites and early morphogenesis in reptile limbs. In Vertebrate Limb and Somite Morphogenesis, Cambridge University Press, London, pp. 373–386
- ^ Tabuchi, Hiroko (2006), Dolphin May Have 'Remains' of Legs, Livescience.com
- ^ Tyson, R.; Graham, J.P.; Colahan, P.T.; Berry, C.R. (2004). "Skeletal atavism in a miniature horse". Veterinary Radiology & Ultrasound. 45 (4): 315–7. doi:10.1111/j.1740-8261.2004.04060.x. PMID 15373256.
- ^ Simpson, G. G. (1951), Horses: The story of the horse family in the modern world and through sixty million years of evolution, Oxford University Press
- ^ Dao, Anh H.; Netsky, Martin G. (1984), "Human tails and pseudotails", Human Pathology, 15 (5): 449–453, doi:10.1016/S0046-8177(84)80079-9, PMID 6373560
- ^ Katja Domes; et al. (2007), "Reevolution of sexuality breaks Dollo's law", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 104 (17): 7139–7144, Bibcode:2007PNAS..104.7139D, doi:10.1073/pnas.0700034104, PMC 1855408, PMID 17438282
- ^ Harris, Matthew P.; et al. (2006), "The Development of Archosaurian First-Generation Teeth in a Chicken Mutant", Current Biology, 16 (4): 371–377, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.12.047, PMID 16488870
- ^ Michael F. Whiting; et al. (2003), "Loss and recovery of wings in stick insects", Nature, 421 (6920): 264–267, Bibcode:2003Natur.421..264W, doi:10.1038/nature01313, PMID 12529642, S2CID 962571
- ^ a b Robert J. Raikow; et al. (1979), "The evolutionary re-establishment of a lost ancestral muscle in the bowerbird assemblage", Condor, 81 (2): 203–206, doi:10.2307/1367290, JSTOR 1367290
- ^ Robert J. Raikow (1975), "The evolutionary reappearance of ancestral muscles as developmental anomalies in two species of birds", Condor, 77 (4): 514–517, doi:10.2307/1366113, JSTOR 1366113
- ^ E. Evansh (1959), "Hyoid muscle anomalies in the dog (Canis familiaris)", Anatomical Record, 133 (2): 145–162, doi:10.1002/ar.1091330204, PMID 13670435, S2CID 33397424
- ^ Castle, William E. (1906), The origin of a polydactylous race of guinea-pigs (49 ed.), Carnegie Institution of Washington
- ^ Held, Lewis I. (2010). "The Evo-Devo Puzzle of Human Hair Patterning". Evolutionary Biology. 37 (2–3): 113–122. doi:10.1007/s11692-010-9085-4. S2CID 12112693.
- ^ a b Futuyma, Douglas J. (1998). Evolutionary Biology (3rd ed.). Sinauer Associates Inc. p. 122. ISBN 978-0-87893-189-7.
- ^ a b 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution: Part 1. Talkorigins.org. Retrieved on 6 December 2011.
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution is True. Viking. pp. 8–11. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Darwin, Charles (1859). On the Origin of Species. John Murray. p. 420.
- ^ Tuomi, J. (1981). "Structure and dynamics of Darwinian evolutionary theory" (PDF). Syst. Zool. 30 (1): 22–31. doi:10.2307/2992299. JSTOR 2992299.
- ^ Aravind, L.; Iyer, L.M.; Anantharaman, V. (2003). "The two faces of Alba: the evolutionary connection between proteins participating in chromatin structure and RNA metabolism". Genome Biology. 4 (10): R64. doi:10.1186/gb-2003-4-10-r64. PMC 328453. PMID 14519199.
- ^ Brochu, C. A.; Wagner, J. R.; Jouve, S.; Sumrall, C. D.; Densmore, L. D. (2009). "A correction corrected:Consensus over the meaning of Crocodylia and why it matters" (PDF). Syst. Biol. 58 (5): 537–543. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syp053. PMID 20525607. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2013.
- ^ Bock, W. J. (2007). "Explanations in evolutionary theory". J Zool Syst Evol Res. 45 (2): 89–103. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0469.2007.00412.x.
- ^ Kluge 1999
- ^ Laurin 2000
- ^ Fitzhugh 2006, p. 31
- ^ Kluge 1999, p. 432
- ^ Slifkin, Natan (2006). The Challenge of Creation…. Zoo Torah. pp. 258–9. ISBN 978-1-933143-15-6.
- ^ Senter, Phil; et al. (2015), "Vestigial Biological Structures: A Classroom-Applicable Test of Creationist Hypotheses", The American Biology Teacher, 77 (2): 99–106, doi:10.1525/abt.2015.77.2.4, S2CID 85573136
- ^ Attila Regoes; et al. (2005), "Protein Import, Replication, and Inheritance of a Vestigial Mitochondrion", The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280 (34): 30557–30563, doi:10.1074/jbc.M500787200, PMID 15985435
- ^ Sekiguchi, Hiroshi; et al. (2002), "Vestigial chloroplasts in heterotrophic stramenopiles Pteridomonas danica and Ciliophrys infusionum (Dictyochophyceae)", Protist, 153 (2): 157–167, doi:10.1078/1434-4610-00094, PMID 12125757
- ^ Paula J. Rudall; et al. (2002), "Floral Anatomy and Systematics of Alliaceae with Particular Reference to Gilliesia, A Presumed Insect Mimic with Strongly Zygomorphic Flowers", American Journal of Botany, 89 (12): 1867–1883, doi:10.3732/ajb.89.12.1867, PMID 21665616
- ^ Strittmatter, Lara I.; et al. (2002), "Subdioecy in Consolea Spinosissima (Cactaceae): Breeding System and Embryological Studies", American Journal of Botany, 89 (9): 1373–1387, doi:10.3732/ajb.89.9.1373, PMID 21665739, S2CID 17169760
- ^ Ashman, Tia-Lynn (2003), "Constraints on the Evolution of Males and Sexual Dimorphism: Field Estimates of Genetic Architecture of Reproductive Traits in Three Populations of Gynodioecious Fragaria virginiana", Evolution, 57 (9): 2012–2025, doi:10.1554/02-493, PMID 14575323, S2CID 198153247
- ^ Golonka, Annette M.; et al. (2005), "Wind Pollination, Sexual Dimorphism, and Changes in Floral Traits of Schiedea (Caryophyllaceae)", American Journal of Botany, 92 (9): 1492–1502, doi:10.3732/ajb.92.9.1492, PMID 21646167
- ^ Walker-Larsen, J.; Harder, L. D. (2001), "Vestigial organs as opportunities for functional innovation: the example of the Penstemon staminode", Evolution, 55 (3): 477–487, doi:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2001.tb00782.x, PMID 11327156, S2CID 19533785
- ^ Gomez, Nadilla N.; Shaw, Ruth G. (2006), "Inbreeding Effect on Male and Female Fertility and Inheritance of Male Sterility in Nemophila menziesii (Hydrophyllaceae)", American Journal of Botany, 93 (5): 739–746, doi:10.3732/ajb.93.5.739, PMID 21642137
- ^ Bejder, Lars; Hall, Brian K. (2002), "Limbs in Whales and Limblessness in Other Vertebrates: Mechanisms ofEvolutionary and Developmental Transformation and Loss", Evolution and Development, 4 (6): 445–458, doi:10.1046/j.1525-142x.2002.02033.x, PMID 12492145, S2CID 8448387
- ^ a b Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution Is True. Viking. pp. 60. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ West-Eberhard, Mary Jane (2003). Developmental plasticity and evolution. Oxford University Press. p. 232. ISBN 978-0-19-512234-3.
- ^ P. C. Simões-Lopes; C. S. Gutstein (2004), "Notes on the anatomy, positioning and homology of the pelvic bones in small cetaceans (Cetacea, Delphinidae, Pontoporiidae)", Latin American Journal of Aquatic Mammals, 3 (2): 157–162, doi:10.5597/lajam00060
- ^ "Example 1: Living whales and dolphins found with hindlimbs". Douglas Theobald. Retrieved 20 March 2011.
- ^ Garner, Stephane; et al. (2006), "Hybridization, developmental stability, and functionality of morphological traits in the ground beetle Carabus solieri (Coleoptera, Carabidae)", Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 89: 151–158, doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2006.00668.x
- ^ Jeffery, William R. (2008), "Emerging model systems in evo-devo: cavefish and microevolution of development", Evolution and Development, 10 (3): 256–272, doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00235.x, PMC 3577347, PMID 18460088
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution Is True. Viking. pp. 59–60. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Abed E. Zubidat; et al. (2010), "Photoentrainment in blind and sighted rodent species: responses to photophase light with different wavelengths", The Journal of Experimental Biology, 213 (Pt 24): 4213–4222, doi:10.1242/jeb.048629, PMID 21113002
- ^ Kearney, Maureen; Maisano, Jessica Anderson; Rowe, Timothy (2005), "Cranial Anatomy of the Extinct Amphisbaenian Rhineura hatcherii (Squamata, Amphisbaenia) Based on High-Resolution X-ray Computed Tomography", Journal of Morphology, 264 (1): 1–33, doi:10.1002/jmor.10210, PMID 15549718, S2CID 7504517
- ^ David C. Culver (1982), Cave Life: Evolution and Ecology, Harvard University Press, ISBN 9780674330191
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution Is True. Viking. pp. 57–59. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Erin E. Maxwell; Hans C.E. Larsson (2007), "Osteology and myology of the wing of the Emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae), and its bearing on the evolution of vestigial structures", Journal of Morphology, 268 (5): 423–441, doi:10.1002/jmor.10527, PMID 17390336, S2CID 12494187
- ^ Michael G. Glasspool (1982), Atlas of Ophthalmology (1 ed.), MTP Press Unlimited, p. 9
- ^ Rehoreka, Susan J.; Smith, Timothy D. (2006), "The primate Harderian gland: Does it really exist?", Ann Anat, 188 (4): 319–327, doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2006.01.018, PMID 16856596
- ^ Andrade, Julia B.; Lewis, Ryshonda P.; Senter, Phil (2016), "Appendicular skeletons of five Asian skink species of the genera Brachymeles and Ophiomorus, including species with vestigial appendicular structures", Amphibia-Reptilia, 37 (4): 337–344, doi:10.1163/15685381-00003062
- ^ Maureen Kearney (2002), "Appendicular Skeleton in Amphisbaenians (Reptilia: Squamata)", Copeia, 2002 (3): 719–738, doi:10.1643/0045-8511(2002)002[0719:asiars]2.0.co;2, S2CID 85768695
- ^ Tsuihiji, Takanobu; Kearney, Maureen; Olivier Rieppel (2006), "First Report of a Pectoral Girdle Muscle in Snakes, with Comments on the Snake Cervico-dorsal Boundary", Copeia, 2006 (2): 206–215, doi:10.1643/0045-8511(2006)6[206:froapg]2.0.co;2, S2CID 85991116
- ^ Mcgowan, Michael R.; Clark, Clay; Gatesy, John (2008), "The Vestigial Olfactory Receptor Subgenome of Odontocete Whales: Phylogenetic Congruence between Gene-Tree Reconciliation and Supermatrix Methods", Systematic Biology, 57 (4): 574–590, doi:10.1080/10635150802304787, PMID 18686195
- ^ Nweeia, Martin T.; et al. (2012), "Vestigial Tooth Anatomy and Tusk Nomenclature for Monodon Monoceros", The Anatomical Record, 295 (6): 1006–1016, doi:10.1002/ar.22449, PMID 22467529, S2CID 22907605
- ^ Tague, Robert G. (2002), "Variability of Metapodials in PrimatesWith Rudimentary Digits: Ateles geoffroyi, Colobus guereza, and Perodicticus potto", American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 117 (3): 195–208, doi:10.1002/ajpa.10028, PMID 11842399
- ^ Peterková, R.; et al. (2002), "Development of the Vestigial Tooth Primordia as Part of Mouse Odontogenesis", Connective Tissue Research, 43 (2–3): 120–128, doi:10.1080/03008200290000745, PMID 12489147, S2CID 33141711
- ^ Liman, Emily R.; Innan, Hideki (2003), "Relaxed selective pressure on an essential component of pheromone transduction in primate evolution", PNAS, 100 (6): 3328–3332, Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.3328L, doi:10.1073/pnas.0636123100, PMC 152292, PMID 12631698
- ^ Zhang, Jianzhi; Webb, David M. (2003), "Evolutionary deterioration of the vomeronasal pheromone transduction pathway in catarrhine primates", PNAS, 100 (14): 8337–8341, Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.8337Z, doi:10.1073/pnas.1331721100, PMC 166230, PMID 12826614
- ^ Tamatsu; et al. (2007), "Vestiges of vibrissal capsular muscles exist in the human upper lip", Clinical Anatomy, 20 (6): 628–631, doi:10.1002/ca.20497, PMID 17458869, S2CID 21055062
- ^ Mbaka, Godwin O.; Ejiwunmi, Adedayo B. (2009), "Prevalence of palmaris longus absence – a study in the Yoruba population", Ulster Medical Journal, 78 (2): 90–93, PMC 2699194, PMID 19568443
- ^ Drouin, Guy; et al. (2011), "The Genetics of Vitamin C Loss in Vertebrates", Current Genomics, 12 (5): 371–378, doi:10.2174/138920211796429736, PMC 3145266, PMID 22294879
- ^ Gibert, Jean-Michel; et al. (2000), "Barnacle Duplicate Engrailed genes: Divergent Expression Patterns and Evidence for a Vestigial Abdomen", Evolution and Development, 2 (4): 194–202, doi:10.1046/j.1525-142x.2000.00059.x, PMID 11252562, S2CID 41665533
- ^ Freyer, Claudia; Renfree, Marilyn B. (2009), "The mammalian yolk sac placenta", Journal of Experimental Zoology, 312B (6): 545–554, doi:10.1002/jez.b.21239, PMID 18985616
- ^ Brawand, David; et al. (2008), "Loss of Egg Yolk Genes in Mammals and the Origin of Lactation and Placentation", PLOS Biology, 6 (3): e63, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060063, PMC 2267819, PMID 18351802
- ^ Myers, P. Z. (2008), "Reproductive history writ in the genome", Pharyngula, ScienceBlogs
- ^ David Seder; et al. (1997), "On the development of Cetacean extremities: I. Hind limb rudimentation in the Spotted dolphin (Stenella attenuata)", European Journal of Morphology, 35 (1): 25–30, doi:10.1076/ejom.35.1.25.13058, PMID 9143876
- ^ Boke, Norman H.; Anderson, Edward F. (1970), "Structure, Development, and Taxonomy in the Genus Lophophora", American Journal of Botany, 57 (5): 569–578, doi:10.2307/2441055, JSTOR 2441055
- ^ Malte Elbrächter; Eberhart Schnepf (1996), "Gymnodinium chlorophorum, a new, green, bloom-forming dino agellate (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae) with a vestigial prasinophyte endosymbiont", Phycologia, 35 (5): 381–393, doi:10.2216/i0031-8884-35-5-381.1
- ^ Jeffrey S. Prince; Paul Micah Johnson (2006), "Ultrastructural Comparison of Aplysia and Dolabrifera Ink Glands Suggests Cellular Sites of Anti-Predator Protein Production and Algal Pigment Processing", Journal of Molluscan Studies, 72 (4): 349–357, doi:10.1093/mollus/eyl017
- ^ Ridley, Mark (2004). Evolution (3rd ed.). Blackwell Publishing. p. 282. ISBN 978-1-4051-0345-9.
- ^ a b Dawkins, Richard (2009). The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution. Bantam Press. pp. 364–365. ISBN 978-1-4165-9478-9.
- ^ Williams, G.C. (1992). Natural selection: domains, levels, and challenges. Oxford Press. ISBN 978-0-19-506932-7.
- ^ "Confessions of a Darwinist". Niles Eldredge. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution is True. Viking. pp. 26–28. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Donald R. Prothero (2013), Bringing Fossils to Life: An Introduction to Paleobiology (3rd ed.), Columbia University Press, p. 21
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". The Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County Foundation. Archived from the original on 11 March 2011. Retrieved 21 February 2011.
- ^ Dean, William Richard John; Milton, Suzanne Jane (1999). The Karoo: Ecological Patterns and Processes. Cambridge University Press. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-521-55450-3.
- ^ Schadewald, Robert J. (1982). "Six "Flood" Arguments Creationists Can't Answer". Creation Evolution Journal. 3: 12–17. Archived from the original on 19 September 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2011.
- ^ a b Donald R. Prothero (2008), "What missing link?", New Scientist, 197 (2645): 35–41, doi:10.1016/s0262-4079(08)60548-5
- ^ "Obviously vertebrates must have had ancestors living in the Cambrian, but they were assumed to be invertebrate forerunners of the true vertebrates — protochordates. Pikaia has been heavily promoted as the oldest fossil protochordate." Richard Dawkins 2004 The Ancestor's Tale Page 289, ISBN 0-618-00583-8
- ^ Chen, J. Y.; Huang, D. Y.; Li, C. W. (1999). "An early Cambrian craniate-like chordate". Nature. 402 (6761): 518–522. Bibcode:1999Natur.402..518C. doi:10.1038/990080. S2CID 24895681.
- ^ Shu, D. G.; Conway Morris, S.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z. F.; Yasui, K.; Janvier, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. L.; Liu, J. N.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. -Q. (2003), "Head and backbone of the Early Cambrian vertebrate Haikouichthys", Nature, 421 (6922): 526–529, Bibcode:2003Natur.421..526S, doi:10.1038/nature01264, PMID 12556891, S2CID 4401274
- ^ Legendre, Serge (1989). Les communautés de mammifères du Paléogène (Eocène supérieur et Oligocène) d'Europe occidentale : structures, milieux et évolution. München: F. Pfeil. p. 110. ISBN 978-3-923871-35-3.
- ^ Academy of Natural Sciences - Joseph Leidy - American Horses Archived 5 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Shubin, Neil (2008). Your Inner Fish. Pantheon. ISBN 978-0-375-42447-2.
- ^ Niedzwiedzki, G.; Szrek, P.; Narkiewicz, K.; Narkiewicz, M.; Ahlberg, P. (2010). "Tetrapod trackways from the early Middle Devonian period of Poland". Nature. 463 (7227): 43–48. Bibcode:2010Natur.463...43N. doi:10.1038/nature08623. PMID 20054388. S2CID 4428903.
- ^ Cota-Sánchez, J. Hugo; Bomfim-Patrício, Márcia C. (2010). "Seed morphology, polyploidy and the evolutionary history of the epiphytic cactus Rhipsalis baccifera (Cactaceae)" (PDF). Polibotanica. 29: 107–129. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2018. Retrieved 28 February 2013.
- ^ Menkhorst, Peter; Knight, Frank (2001). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Australia. Oxford University Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-19-550870-3.
- ^ Augee, Michael; Gooden, Brett; Musser, Anne (2006). Echidna: Extraordinary egg-laying mammal. CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 9780643092044.
- ^ "Polar Bears/Habitat & Distribution". SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment. Archived from the original on 25 October 2013. Retrieved 21 February 2011.
- ^ "Sirenians of the World". Save the Manatee Club. Archived from the original on 26 October 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2011.
- ^ Continental Drift and Evolution Archived 11 February 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Biology.clc.uc.edu (25 March 2001). Retrieved on 2011-12-06.
- ^ a b c d Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution is True. Viking. pp. 99–110. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Murphy, James B.; Ciofi, Claudio; de la Panouse, Colomba; Walsh, Trooper, eds. (2002). Komodo Dragons: Biology and Conservation (Zoo and Aquarium Biology and Conservation Series). Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Books. ISBN 978-1-58834-073-3.
- ^ Burdick, Alan (25 March 2007). "The Wonder Land of Socotra, Yemen". ALAN BURDICK. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ "Tuatara". New Zealand Ecology: Living Fossils. TerraNature Trust. 2004. Retrieved 10 November 2006.
- ^ "Facts about tuatara". Conservation: Native Species. Threatened Species Unit, Department of Conservation, Government of New Zealand. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 10 February 2007.
- ^ "New Caledonia's most wanted". Archived from the original on 29 September 2018. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ "Giant bushy-tailed cloud rat (Crateromys schadenbergi)". Archived from the original on 30 June 2010. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ Rabor, D.S. (1986). Guide to Philippine Flora and Fauna. Natural Resources Management Centre, Ministry of Natural Resources and University of the Philippines.
- ^ Humphrey, Robert R. (1974). The Boojum and its Home. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0816504367.
- ^ Schofield, James (27 July 2001). "Lake Baikal's Vanishing Nerpa Seal". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
- ^ Baldwin, B. G.; Robichaux, R. H. (1995). "Historical biogeography and ecology of the Hawaiian silversword alliance (Asteraceae). New molecular phylogenetic perspectives". In Wagner, W. L.; Funk, V. A. (eds.). Hawaiian biogeography: evolution on a hotspot archipelago. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press. pp. 259–287.
- ^ "Adaptive Radiation and Hybridization in the Hawaiian Silversword Alliance". University of Hawaii Botany Department.
- ^ Pallen, Mark (2009). Rough Guide to Evolution. Rough Guides. p. 87. ISBN 978-1-85828-946-5.
- ^ Irwin, D.E.; Irwin, J.H.; Price, T.D. (2001). "Ring species as bridges between microevolution and speciation". Genetica. 112–113: 223–43. doi:10.1023/A:1013319217703. PMID 11838767. S2CID 7108000. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 May 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ^ Dawkins, Richard (2004). The Ancestor's Tale. Houghton Mifflin. p. 303. ISBN 978-0-618-00583-3.
- ^ Davis, Paul and Kenrick, Paul. 2004. Fossil Plants. Smithsonian Books (in association with the Natural History Museum of London), Washington, D.C. ISBN 1-58834-156-9
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution is True. Viking. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Pioneer Productions (19 January 2010). "Episode Guide". How The Earth Was Made. Season 2. Episode 8. History channel.
- ^ Luo, Zhe-Xi; Ji, Qiang; Wible, John R.; Yuan, Chong-Xi (12 December 2003). "An early Cretaceous tribosphenic mammal and metatherian evolution". Science. 302 (5652): 1934–1940. Bibcode:2003Sci...302.1934L. doi:10.1126/science.1090718. PMID 14671295. S2CID 18032860.
- ^ Nilsson, M. A.; Churakov, G.; Sommer, M.; Van Tran, N.; Zemann, A.; Brosius, J.; Schmitz, J. (27 July 2010). Penny, David (ed.). "Tracking Marsupial Evolution Using Archaic Genomic Retroposon Insertions". PLOS Biology. 8 (7): e1000436. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000436. PMC 2910653. PMID 20668664.
- ^ Woodburne, Michael O.; Zinsmeister, William J. (October 1982). "Fossil Land Mammal from Antarctica". Science. 218 (4569): 284–286. Bibcode:1982Sci...218..284W. doi:10.1126/science.218.4569.284. PMID 17838631. S2CID 32304737.
- ^ Goin, Francisco J.; et al. (December 1999). "New Discoveries of "Opposum-Like" Marsupials from Antarctica (Seymour Island, Medial Eocene)". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 6 (4): 335–365. doi:10.1023/A:1027357927460. S2CID 2319361.
- ^ Reguero, Marcelo A.; Marenssi, Sergio A.; Santillana, Sergio N. (May 2002). "Antarctic Peninsula and South America (Patagonia) Paleogene terrestrial faunas and environments: biogeographic relationships". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 179 (3–4): 189–210. Bibcode:2002PPP...179..189R. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00417-5.
- ^ Mills, William James. Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, 2003. ISBN 1-57607-422-6, ISBN 978-1-57607-422-0
- ^ Goin, F.J.; Reguero, M.A.; Pascual, R.; von Koenigswald, W.; Woodburne, M.O.; Case, J.A.; Marenssi, S.A.; Vieytes, C.; Vizcaíno, S.F. (2006). "First gondwanatherian mammal from Antarctica". Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 258 (1): 135–144. Bibcode:2006GSLSP.258..135G. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.258.01.10. S2CID 129493664.
- ^ Prothero, Donald R.; Schoch, Robert M. (2002). Horns, tusks, and flippers: the evolution of hoofed mammals. JHU press. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-8018-7135-1.
- ^ a b James M. Sobel; et al. (2009), "The Biology of Speciation", Evolution, 64 (2): 295–315, doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2009.00877.x, PMID 19891628, S2CID 10168162
- ^ a b Jerry A. Coyne; H. Allen Orr (2004), Speciation, Sinauer Associates, p. 5, ISBN 978-0-87893-089-0
- ^ Raven, Peter H. (2005). Biology of Plants (7th rev. ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-6284-3. OCLC 183148564.
- ^ Haas, J. W. Jr. (June 2000). "The Rev. Dr. William H. Dallinger F.R.S.: Early Advocate of Theistic Evolution and Foe of Spontaneous Generation". Perspectives on Science and Christian Faith. 52: 107–117. Retrieved 15 June 2010.
- ^ a b Le Page, Michael (16 April 2008). "NS:bacteria make major evolutionary shift in the lab". New Scientist. Retrieved 9 July 2012.
- ^ Blount Z.D.; Borland C.Z.; Lenski, R.E. (June 2008). "Historical contingency and the evolution of a key innovation in an experimental population of Escherichia coli". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 (23): 7899–906. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.7899B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0803151105. PMC 2430337. PMID 18524956.
- ^ Lenski, Richard E.; Travisano, Michael (1994). "Dynamics of adaptation and diversification: A 10,000-generation experiment with bacterial populations". PNAS. 91 (15): 6808–6814. Bibcode:1994PNAS...91.6808L. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.15.6808. PMC 44287. PMID 8041701.
- ^ Turko, Patrick; et al. (2016), "Rapid Evolutionary Loss of Metal Resistance Revealed by Hatching Decades-Old Eggs", Evolution, 70 (2): 398–407, doi:10.1111/evo.12859, PMID 26768308, S2CID 205124469
- ^ Rudge, David W. (2005). "The Beauty of Kettlewell's Classic Experimental Demonstration of Natural Selection". BioScience. 55 (4): 369–375. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2005)055[0369:TBOKCE]2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Majerus, Michael E. N. (2008). "Industrial Melanism in the Peppered Moth, Biston betularia: An Excellent Teaching Example of Darwinian Evolution in Action" (PDF). Evolution: Education and Outreach. 2 (1): 63–74. doi:10.1007/s12052-008-0107-y. S2CID 25407417.
- ^ Tanaka, T.; Hashimoto, H. (1989). "Drug-resistance and its transferability of Shigella strains isolated in 1986 in Japan". Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 63 (1): 15–26. doi:10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.63.15. PMID 2501419.
- ^ Thwaites, W.M. (Summer 1985). "New Proteins Without God's Help". Creation Evolution Journal. 5 (2): 1–3.
- ^ Evolution and Information: The Nylon Bug. Nmsr.org. Retrieved on 6 December 2011.
- ^ Than, Ker (23 September 2005). "Why scientists dismiss 'intelligent design". NBC News.
- ^ Miller, Kenneth R. Only a Theory: Evolution and the Battle for America's Soul (2008) pp. 80–82
- ^ Sean Stankowski; Matthew A. Streisfeld (2015), "Introgressive hybridization facilitates adaptive divergence in a recent radiation of monkeyflowers", Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 282 (1814): 20151666, doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.1666, PMC 4571715, PMID 26311673
- ^ Science News, Dark Power: Pigment seems to put radiation to good use, Week of 26 May 2007; Vol. 171, No. 21, p. 325 by Davide Castelvecchi
- ^ Dadachova, E.; Bryan, R.A.; Huang, X.; Moadel, T.; Schweitzer, A.D.; Aisen, P.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A. (2007). Rutherford, Julian (ed.). "Ionizing Radiation Changes the Electronic Properties of Melanin and Enhances the Growth of Melanized Fungi". PLOS ONE. 2 (5): e457. Bibcode:2007PLoSO...2..457D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000457. PMC 1866175. PMID 17520016.
- ^ a b John A. Endler (1980). "Natural Selection on Color Patterns in Poecilia reticulata". Evolution. 34 (1): 76–91. doi:10.2307/2408316. JSTOR 2408316. PMID 28563214.
- ^ David N. Reznick; Frank H. Shaw; F. Helen Rodd; Ruth G. Shaw (1997). "Evaluation of the Rate of Evolution in Natural Populations of Guppies (Poecilia reticulata)". Science. 275 (5308): 1934–1937. doi:10.1126/science.275.5308.1934. PMID 9072971. S2CID 18480502.
- ^ David Reznick; John A. Endler (1982). "The Impact of Predation on Life History Evolution in Trinidadian Guppies (Poecilia reticulata)". Evolution. 36 (1): 160–177. doi:10.2307/2407978. JSTOR 2407978. PMID 28581096.
- ^ Medical Research Council (UK) (21 November 2009). "Brain Disease 'Resistance Gene' Evolves in Papua New Guinea Community; Could Offer Insights Into CJD". Science Daily (online). Science News. Retrieved 22 November 2009.
- ^ Mead, S.; Whitfield, J.; Poulter, M.; Shah, P.; Uphill, J.; Campbell, T.; Al-Dujaily, H.; Hummerich, H.; Beck, J.; Mein, C. A.; Verzilli, C.; Whittaker, J.; Alpers, M. P.; Collinge, J. (2009). "A Novel Protective Prion Protein Variant that Colocalizes with Kuru Exposure" (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (21): 2056–2065. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0809716. PMID 19923577.
- ^ Byars, S. G.; Ewbank, D.; Govindaraju, D. R.; Stearns, S. C. (2009). "Natural selection in a contemporary human population". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (suppl_1): 1787–1792. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.1787B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906199106. PMC 2868295. PMID 19858476.
- ^ Soy and Lactose Intolerance Wayback: Soy Nutrition
- ^ Enattah, N.S.; Sahi, T.; Savilahti, E.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Peltonen, L.; Järvelä, I. (2002). "Identification of a variant associated with adult-type hypolactasia". Nature Genetics. 30 (2): 233–7. doi:10.1038/ng826. PMID 11788828. S2CID 21430931.
- ^ Curry, Andrew (31 July 2013). "Archaeology: The milk revolution". Nature. 500 (7460): 20–2. Bibcode:2013Natur.500...20C. doi:10.1038/500020a. PMID 23903732.
- ^ Swallow DM (2003). "Genetics of lactase persistence and lactose intolerance". Annual Review of Genetics. 37: 197–219. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.37.110801.143820. PMID 14616060.
- ^ Harriet, Coles (20 January 2007). "The lactase gene in Africa: Do you take milk?". The Human Genome, Wellcome Trust. Archived from the original on 29 September 2008. Retrieved 18 July 2008.
- ^ Tishkoff, S.A.; Reed, F.A.; Ranciaro, A.; et al. (January 2007). "Convergent adaptation of human lactase persistence in Africa and Europe". Nature Genetics. 39 (1): 31–40. doi:10.1038/ng1946. PMC 2672153. PMID 17159977.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Herrel, A.; Huyghe, K.; Vanhooydonck, B.; et al. (March 2008). "Rapid large-scale evolutionary divergence in morphology and performance associated with exploitation of a different dietary resource". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 (12): 4792–5. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.4792H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711998105. PMC 2290806. PMID 18344323.
- ^ a b c d Bart Vervust; Irena Grbac; Raoul Van Damme (August 2007). "Differences in morphology, performance and behaviour between recently diverged populations of Podarcis sicula mirror differences in predation pressure". Oikos. 116 (8): 1343–1352. doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15989.x. S2CID 55765174.
- ^ "Lizards Rapidly Evolve After Introduction to Island". National Geographic. 21 April 2008. Archived from the original on 23 April 2008.
- ^ Myers, PZ (23 April 2008). "Still just a lizard". ScienceBlogs.
- ^ Clark, Bryan W.; et al. (2013). "Compound- and Mixture-Specific Differences in Resistance to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and PCB-126 among Fundulus heteroclitus Subpopulations throughout the Elizabeth River Estuary". Environmental Science & Technology. 47 (18): 10556–10566. doi:10.1021/es401604b. PMC 4079253. PMID 24003986.
- ^ Welsh, Jennifer (17 February 2011). "Fish Evolved to Survive GE Toxins in Hudson River". LiveScience. Retrieved 19 February 2011.
- ^ a b c Isaac Wirgin; et al. (2011). "Mechanistic Basis of Resistance to PCBs in Atlantic Tomcod from the Hudson River". Science. 331 (6022): 1322–1325. Bibcode:2011Sci...331.1322W. doi:10.1126/science.1197296. PMC 3246799. PMID 21330491.
- ^ Cheptou, P.; Carrue, O.; Rouifed, S.; Cantarel, A. (2008). "Rapid evolution of seed dispersal in an urban environment in the weed Crepis sancta". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (10): 3796–9. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.3796C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708446105. PMC 2268839. PMID 18316722.
- ^ "Evolution in the urban jungle". Archived from the original on 8 November 2012. Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- ^ "Human Activity Boosts Brain Size in Animals". Yale Scientific. 21 December 2013. Retrieved 16 March 2015.
- ^ Snell-Rood, Emilie C.; Wick, Naomi (2013). "Anthropogenic environments exert variable selection on cranial capacity in mammals". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 280 (1769): 20131384. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.1384. PMC 3768300. PMID 23966638.
- ^ a b c Rosenblum, Erica Bree (2006), "Convergent Evolution and Divergent Selection: Lizards at the White Sands Ecotone", The American Naturalist, 167 (1): 1–15, doi:10.1086/498397, PMID 16475095, S2CID 10765531
- ^ Rosenblum, Erica Bree (2007), "A multilocus perspective on colonization accompanied by selection and gene flow", Evolution, 61 (12): 2971–2985, doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00251.x, PMID 17976180, S2CID 2322067
- ^ a b c Des Roches, Simone (2014), "Beyond black and white: divergent behaviour and performance in three rapidly evolving lizard species at White Sands", Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 111: 169–182, doi:10.1111/bij.12165
- ^ a b c Robertson, Jeanne Marie (2009), "Rapid divergence of social signal coloration across the White Sands ecotone for three lizard species under strong natural selection", Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 98 (2): 243–255, doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2009.01291.x
- ^ Schemske, Douglas W. (2000), "Understanding the Origin of Species", Evolution, 54 (3): 1069–1073, doi:10.1554/0014-3820(2000)054[1069:utoos]2.3.co;2, S2CID 85083567
- ^ Mallet, James (2001), "The Speciation Revolution", Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 14 (6): 887–888, doi:10.1046/j.1420-9101.2001.00342.x, S2CID 36627140
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A.; Orr, H. Allen (2004), Speciation, Sinauer Associates, p. 37, ISBN 978-0-87893-089-0
- ^ Florin, A.-B.; A. Ödeen (2002), "Laboratory environments are not conducive for allopatric speciation", Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 15: 10–19, doi:10.1046/j.1420-9101.2002.00356.x, S2CID 85410953
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A.; Orr, H. Allen (2004), Speciation, Sinauer Associates, pp. 88–89, ISBN 978-0-87893-089-0
- ^ Liebherr, James K.; McHugh, Joseph V. in Resh, V. H.; Cardé, R. T. (Editors) 2003. Encyclopedia of Insects. Academic Press.
- ^ a b c d e f Benton, Michael J.; Pearson, Paul N. (2001), "Speciation in the Fossil Record", Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16 (7): 405–411, doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02149-8, PMID 11403874
- ^ Erwin, D. H. & Anstey, R. L. (1995), New Approaches to Speciation in the Fossil Record, Columbia University Press, p. 22
- ^ Lazarus, David; et al. (1995), "Sympatric Speciation and Phyletic Change in Globorotalia truncatulinoides", Paleobiology, 21 (1): 28–51, Bibcode:1995Pbio...21...28L, doi:10.1017/s0094837300013063, S2CID 88910977
- ^ Kellogg, Davida E.; Hays, James D. (1975), "Microevolutionary Patterns in Late Cenozoic Radiolaria", Paleobiology, 1 (2): 150–160, Bibcode:1975Pbio....1..150K, doi:10.1017/s0094837300002347, S2CID 88958553
- ^ Hays, James D. (1970), "Stratigraphy and Evolutionary Trends of Radiolaria in North Pacific Deep-Sea Sediments", Geological Society of America Memoirs, 126: 185–218, doi:10.1130/MEM126-p185, ISBN 978-0-8137-1126-3
- ^ Ulf Sörhannus; et al. (1998), "Cladogenetic and anagenetic changes in the morphology of Rhizosolenia praebergonii Mukhina", Historical Biology, 1 (3): 185–205, doi:10.1080/08912968809386474
- ^ Sörhannus, Ulf; et al. (1991), "Iterative evolution in the diatom genus Rhizosolenia Ehrenberg", Lethaia, 24 (1): 39–44, doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1991.tb01178.x
- ^ Pearson, Paul N.; Ezard, Thomas H. G. (2014). "Evolution and speciation in the Eocene planktonic foraminifer Turborotalia" (PDF). Paleobiology. 40: 130–143. doi:10.1666/13004. S2CID 5625312.
- ^ Gingerich, P. D. (1985), "Species in the Fossil Record: Concepts, Trends, and Transitions", Paleobiology, 11 (1): 27–41, Bibcode:1985Pbio...11...27G, doi:10.1017/s0094837300011374, S2CID 88897579
- ^ Gingerich, P. D. (1976), "Paleontology and Phylogeny: Patterns of Evolution at the Species Level in Early Tertiary Mammals", American Journal of Science, 276 (1): 1–28, Bibcode:1976AmJS..276....1G, doi:10.2475/ajs.276.1.1
- ^ Chaline, J.; et al. (1993), "Morphological Trends and Rates of Evolution in Arvicolids (Arvicolidae, Rodentia): Towards a Punctuated Equilibria/Disequilibria Model", Quaternary International, 19: 27–39, Bibcode:1993QuInt..19...27C, doi:10.1016/1040-6182(93)90019-c
- ^ Rice, William R.; Salt, George W. (1990). "The Evolution of Reproductive Isolation as a Correlated Character Under Sympatric Conditions: Experimental Evidence". Evolution. 44 (5): 1140–1152. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1990.tb05221.x. PMID 28563894. S2CID 9145271.
- ^ "The Evolution of Reproductive Isolation as a Correlated Character Under Sympatric Conditions: Experimental Evidence" (PDF). William R. Rice, George W. Salt. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- ^ "Observed Instances of Speciation, 5.3.5 Sympatric Speciation in Drosophila melanogaster". Joseph Boxhorn. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- ^ Scott P. Egan; et al. (2012), "Divergent host-plant use promotes reproductive isolation among cynipid gall wasp populations", Biology Letters, 8 (4): 605–608, doi:10.1098/rsbl.2011.1205, PMC 3391443, PMID 22337505
- ^ Egan, Scott P.; et al. (2013), "Parallel Patterns of Morphological and Behavioral Variation among Host-Associated Populations of Two Gall Wasp Species", PLOS ONE, 8 (1): e54690, Bibcode:2013PLoSO...854690E, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054690, PMC 3549985, PMID 23349952
- ^ Feder, J.L.; Roethele, J.B.; Filchak, K.; Niedbalski, J.; Romero-Severson, J. (1 March 2003). "Evidence for inversion polymorphism related to sympatric host race formation in the apple maggot fly, Rhagoletis pomonella". Genetics. 163 (3): 939–53. doi:10.1093/genetics/163.3.939. PMC 1462491. PMID 12663534.
- ^ Berlocher, S.H.; Bush, G.L. (1982). "An electrophoretic analysis of Rhagoletis (Diptera: Tephritidae) phylogeny". Systematic Zoology. 31 (2): 136–55. doi:10.2307/2413033. JSTOR 2413033.
- ^ Berlocher, S.H.; Feder, J.L. (2002). "Sympatric speciation in phytophagous insects: moving beyond controversy?". Annu Rev Entomol. 47: 773–815. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145312. PMID 11729091. S2CID 9677456.
- ^ Bush, G.L. (1969). "Sympatric host race formation and speciation in frugivorous flies of the genus Rhagoletis (Diptera: Tephritidae)". Evolution. 23 (2): 237–51. doi:10.2307/2406788. JSTOR 2406788. PMID 28562891.
- ^ Prokopy, R.J.; Diehl, S.R.; Cooley, S.S. (1988). "Behavioral evidence for host races in Rhagoletis pomonella flies" (PDF). Oecologia. 76 (1): 138–47. Bibcode:1988Oecol..76..138P. doi:10.1007/BF00379612. hdl:2027.42/47773. JSTOR 4218647. PMID 28312391. S2CID 19076040.
- ^ Feder, J.L.; Roethele, J.B.; Wlazlo, B.; Berlocher, S.H. (1997). "Selective maintenance of allozyme differences among sympatric host races of the apple maggot fly". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94 (21): 11417–21. Bibcode:1997PNAS...9411417F. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.21.11417. PMC 23485. PMID 11038585.
- ^ a b c "London underground source of new insect forms". The Times. 26 August 1998.
- ^ a b Fonseca, D. M.; Keyghobadi, N; Malcolm, CA; Mehmet, C; Schaffner, F; Mogi, M; Fleischer, RC; Wilkerson, RC (2004). "Emerging vectors in the Culex pipiens complex" (PDF). Science. 303 (5663): 1535–8. Bibcode:2004Sci...303.1535F. doi:10.1126/science.1094247. PMID 15001783. S2CID 40158868. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2011.
- ^ a b Burdick, Alan (2001). "Insect From the Underground — London, England Underground home to different species of mosquitos". Natural History.
- ^ Byrne, K.; Nichols, R.A. (1999). "Culex pipiens in London Underground tunnels: differentiation between surface and subterranean populations". Heredity. 82 (1): 7–15. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6884120. PMID 10200079.
- ^ Vinogradova, E.B.; Shaikevich, E.V. (2007). "Morphometric, physiological and molecular characteristics of underground populations of the urban mosquito Culex pipiens Linnaeus f. molestus Forskål (Diptera: Culicidae) from several areas of Russia" (PDF). European Mosquito Bulletin. 22: 17–24.
- ^ a b c Hurt, Carla; et al. (2008), "A Multilocus Test of Simultaneous Divergence Across the Isthmus of Panama Using Snapping Shrimp in the Genus Alpheus", Evolution, 63 (2): 514–530, doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00566.x, PMID 19154357, S2CID 11820649
- ^ C. Montes; et al. (2015), "Middle Miocene closure of the Central American Seaway", Science, 348 (6231): 226–229, Bibcode:2015Sci...348..226M, doi:10.1126/science.aaa2815, PMID 25859042
- ^ Knowlton, Nancy (1993), "Divergence in Proteins, Mitochondrial DNA, and Reproductive Compatibility Across the Isthmus of Panama", Science, 260 (5114): 1629–1632, Bibcode:1993Sci...260.1629K, doi:10.1126/science.8503007, PMID 8503007, S2CID 31875676
- ^ a b Knowlton, Nancy; Weigt, Lee A. (1998), "New dates and new rates for divergence across the Isthmus of Panama", Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, 265 (1412): 2257–2263, doi:10.1098/rspb.1998.0568, PMC 1689526
- ^ a b c Rieseberg, Loren H.; Wendel, Jonathan (2004), "Plant Speciation - Rise of the Poor Cousins", New Phytologist, 161: 1–21, doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.00957.x
- ^ a b Lafon-Placette, Clément; et al. (2016), "Current plant speciation research: unravelling the processes and mechanisms behind the evolution of reproductive isolation barriers", New Phytologist, 209 (1): 29–33, doi:10.1111/nph.13756, PMID 26625345
- ^ Anacker, Brian L.; Strauss, Sharon Y. (2014), "The Geography and Ecology of Plant Speciation: Range Overlap and Niche Divergence in Sister Species", Proc. R. Soc. B, 281 (1778): 20132980, doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2980, PMC 3906944, PMID 24452025
- ^ Hegarty, Matthew J.; Hiscock, Simon J. (2004), "Hybrid speciation in plants: new insights from molecular studies", New Phytologist, 165 (2): 411–423, doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01253.x, PMID 15720652, S2CID 29320650
- ^ Wendel, Jonathan F. (January 2000). "Genome evolution in polyploids". Plant Molecular Biology. 42 (1): 225–249. doi:10.1023/A:1006392424384. ISSN 0167-4412. PMID 10688139. S2CID 14856314.
- ^ Sémon, Marie; Wolfe, Kenneth H. (December 2007). "Consequences of genome duplication". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 17 (6): 505–512. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2007.09.007. ISSN 0959-437X. PMID 18006297.
- ^ a b Comai, Luca (November 2005). "The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid". Nature Reviews Genetics. 6 (11): 836–846. doi:10.1038/nrg1711. ISSN 1471-0056. PMID 16304599. S2CID 3329282.
- ^ Soltis, Pamela S.; Soltis, Douglas E. (20 June 2000). "The role of genetic and genomic attributes in the success of polyploids". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (13): 7051–7057. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.7051S. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.13.7051. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 34383. PMID 10860970.
- ^ Mavarez, Jesús; Salazar, Camilo A.; Bermingham, Eldredge; et al. (15 June 2006). "Speciation by hybridization in Heliconius butterflies". Nature. 441 (7095): 868–871. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..868M. doi:10.1038/nature04738. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 16778888. S2CID 2457445.
- ^ Ramsey, Justin; Schemske, Douglas W. (November 1998). "Pathways, Mechanisms, and Rates of Polyploid Formation in Flowering Plants". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 29: 467–501. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.467. ISSN 1545-2069. S2CID 31637733.
- ^ Otto, Sarah P.; Whitton, Jeannette (December 2000). "Polyploid Incidence and Evolution". Annual Review of Genetics. 34: 401–437. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.323.1059. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.34.1.401. ISSN 0066-4197. PMID 11092833.
- ^ a b Eric Baack; et al. (2015), "The Origins of Reproductive Isolation in Plants", New Phytologist, 207 (4): 968–984, doi:10.1111/nph.13424, PMID 25944305, S2CID 30147815
- ^ Vallejo-Marín, Mario (2012). "Mimulus peregrinus (Phrymaceae): A new British allopolyploid species". PhytoKeys (14): 1–14. doi:10.3897/phytokeys.14.3305. PMC 3492922. PMID 23170069.
- ^ Vallejo-Marín, Mario; Buggs, Richard J.; Cooley, Arielle M.; Puzey, Joshua R. (2015). "Speciation by genome duplication: Repeated origins and genomic composition of the recently formed allopolyploid species Mimulus peregrinus". Evolution. 69 (6): 1487–1500. doi:10.1111/evo.12678. PMC 5033005. PMID 25929999.
- ^ Karpechenko, G.D. (1927). "Polyploid hybrids of Raphanus sativus X Brassica oleracea L". Bull. Appl. Bot. 17: 305–408.
- ^ Terasawa, Y (1933). "Crossing between Brassico-raphanus and B. chinensis and Raphanus sativus". Japanese Journal of Genetics. 8 (4): 229–230. doi:10.1266/jjg.8.229.
- ^ Lowe, Andrew J.; Abbott, Richard J. (1996). "Origins of the New Allopolyploid Species Senecio camrensis (asteracea) and its Relationship to the Canary Islands Endemic Senecio tenerifae". American Journal of Botany. 83 (10): 1365–1372. doi:10.2307/2446125. JSTOR 2446125.
- ^ Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution is True. Penguin Group. pp. 187–189. ISBN 978-0-670-02053-9.
- ^ Missouri Botanical Garden. "TROPICOS Web display Senecio vulgaris L". Nomenclatural and Specimen Data Base. Missouri State Library. Archived from the original on 2 August 2013. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ a b Bomblies, Kirsten; Lempe, Janne; Epple, Petra; Warthmann, Norman; Lanz, Christa; Dangl, Jeffery L.; Weigel, Detlef (2007). "Autoimmune Response as a Mechanism for a Dobzhansky-Muller-Type Incompatibility Syndrome in Plants". PLOS Biol. 5 (9): e236. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050236. PMC 1964774. PMID 17803357.
- ^ "New plant species arise from conflicts between immune system genes". Ed Yong. Archived from the original on 3 February 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ^ Purves, William Kirkwood; Sadava, David E.; Orians, Gordon H.; Heller, H. Craig (2006). Life, the science of biology (7 ed.). Sinaur Associates, Inc. p. 487. ISBN 978-0-7167-9856-9.
- ^ Soltis, Pam (17 March 2011). "UF researcher: Flowering plant study 'catches evolution in the act'". EurekAlert, American Association for the Advancement of Science. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- ^ Buggs, Richard J.A.; Zhang, Linjing; Miles, Nicholas; Tate, Jennifer A.; Gao, Lu; Wei, Wu; Schnable, Patrick S.; Barbazuk, W. Brad; Soltis, Pamela S. (2011). "Transcriptomic Shock Generates Evolutionary Novelty in a Newly Formed, Natural Allopolyploid Plant". Current Biology. 21 (7): 551–6. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.016. PMID 21419627. S2CID 18417406.
- ^ Bearhop, S.; Fiedler, W.; Furness, R.W.; Votier, S.C.; Waldron, S.; Newton, J.; Bowen, G.J.; Berthold, P.; Farnsworth, K. (2005). "Assortative mating as a mechanism for rapid evolution of a migratory divide". Science. 310 (5747): 502–504. Bibcode:2005Sci...310..502B. doi:10.1126/science.1115661. PMID 16239479. S2CID 6415789. Supporting Online Material
- ^ Yong, Ed (3 December 2009). "British birdfeeders split blackcaps into two genetically distinct groups". ScienceBlogs. Retrieved 21 May 2010.
- ^ Tobler, Michael (2009). "Does a predatory insect contribute to the divergence between cave- and surface-adapted fish populations?". Biology Letters. 5 (4): 506–509. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0272. PMC 2781934. PMID 19443506.
- ^ "Giant insect splits cavefish into distinct populations". Ed Yong. Archived from the original on 1 February 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ^ J. P. Doupé; J. H. England; M. Furze; D. Paetkau (2007), "Most Northerly Observation of a Grizzly Bear (Ursus arctos) in Canada: Photographic and DNA Evidence from Melville Island, Northwest Territories", Arctic, 60: 271–276
- ^ Gray, A. P. (1972), Mammalian hybrids. A check-list with bibliography (2nd ed.), Farnham Royal, Slough SL2 3BN, England: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux
- ^ Kutschera, Verena E; Bidon, Tobias; Hailer, Frank; Rodi, Julia L.; Fain, Steven R.; Janke, Axel (2014). "Bears in a Forest of Gene Trees: Phylogenetic Inference Is Complicated by Incomplete Lineage Sorting and Gene Flow". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 31 (8): 2004–2017. doi:10.1093/molbev/msu186. PMC 4104321. PMID 24903145.
- ^ a b Lindqvist, C.; Schuster, S. C.; Sun, Y.; Talbot, S. L.; Qi, J.; Ratan, A.; Tomsho, L. P.; Kasson, L.; Zeyl, E.; Aars, J.; Miller, W.; Ingolfsson, O.; Bachmann, L.; Wiig, O. (2010). "Complete mitochondrial genome of a Pleistocene jawbone unveils the origin of polar bear". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (11): 5053–7. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.5053L. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914266107. PMC 2841953. PMID 20194737.
- ^ Hailer, F.; Kutschera, V. E.; Hallstrom, B. M.; Klassert, D.; Fain, S. R.; Leonard, J. A.; Arnason, U.; Janke, A. (2012). "Nuclear Genomic Sequences Reveal that Polar Bears Are an Old and Distinct Bear Lineage" (PDF). Science. 336 (6079): 344–7. Bibcode:2012Sci...336..344H. doi:10.1126/science.1216424. hdl:10261/58578. PMID 22517859. S2CID 12671275.
- ^ Liu S.; et al. (2014), "Population genomics reveal recent speciation and rapid evolutionary adaptation in polar bears", Cell, 157 (4): 785–794, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.054, PMC 4089990, PMID 24813606
- ^ Miller, W; Schuster, SC; Welch, AJ; Ratan, A; Bedoya-Reina, OC; Zhao, F; Kim, HL; Burhans, RC; Drautz, DI; Wittekindt, NE; Tomsho, LP; Ibarra-Laclette, E; Herrera-Estrella, L; Peacock, E; Farley, S; Sage, GK; Rode, K; Obbard, M; Montiel, R; Bachmann, L; Ingólfsson, O; Aars, J; Mailund, T; Wiig, O; Talbot, SL; Lindqvist, C (2012). "Polar and brown bear genomes reveal ancient admixture and demographic footprints of past climate change". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (36): E2382–E2390. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109E2382M. doi:10.1073/pnas.1210506109. PMC 3437856. PMID 22826254.
- ^ "Evolution". Polar Bears International. Archived from the original on 30 November 2016. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- ^ Hansman, Jared (6 August 2008). "Adaptive Traits of the Polar Bear (Ursus maritimus)". Helium, Inc. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 30 January 2014.
- ^ a b Tickell, W. L. N. (March 2003). "White Plumage". Waterbirds: The International Journal of Waterbird Biology. 26 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1675/1524-4695(2003)026[0001:wp]2.0.co;2. JSTOR 1522461. S2CID 153315450.
- ^ Larson, Edward J. (2004). Evolution: The Remarkable History of a Scientific Theory. New York: Modern Library. pp. 121–123, 152–157. ISBN 978-0-679-64288-6.
- ^ Bowler, Peter J. (1983). The Eclipse of Darwinism: anti-Darwinian evolutionary theories in the decades around 1900. Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 29, 250. ISBN 978-0-8018-4391-4.
- ^ a b Cott, Hugh B. (1940). Adaptive Coloration in Animals. Methuen. pp. 68–72.
- ^ a b Cook, L. M.; Grant, B. S.; Saccheri, I. J.; Mallet, James (2012). "Selective bird predation on the peppered moth: the last experiment of Michael Majerus". Biology Letters. 8 (4): 609–612. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2011.1136. PMC 3391436. PMID 22319093.
- ^ Brower, Jane Van Zandt (1958). "Experimental studies of mimicry in some North American butterflies: Part I. The monarch, Danaus plexippus, and viceroy, Limenitis archippus archippus". Evolution. 12 (1): 32–47. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1958.tb02926.x. ISSN 0014-3820.
- ^ Brower, Jane Van Zandt (1958). "Experimental studies of mimicry in some North American butterflies: Part II. Battus philenor and Papilio troilus, P. polyxenes and P. glaucus". Evolution. 12 (2): 123–136. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1958.tb02939.x. ISSN 0014-3820.
- ^ Brower, Jane Van Zandt (1958). "Experimental studies of mimicry in some North American butterflies: Part III. ***Danaus gilippus berenice and Limenitis archippus floridensis". Evolution. 12 (3): 273–285. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1958.tb02959.x. ISSN 0014-3820.
- ^ Wallace, Alfred Russel (2015) [1889]. Darwinism - An Exposition Of The Theory Of Natural Selection - With Some Of Its Applications. Read Books. p. 180. ISBN 978-1-4733-7510-9.
- ^ Poulton, Edward Bagnall (1890). The Colours of Animals. p. Foldout after page 339, and throughout.
- ^ Peckre, Louise; Fabre1, Anne-Claire; Wall, Christine E; Brewer, David; Ehmke, Erin; Haring, David; Shaw, Erin; Welser, Kay; Pouydebat, Emmanuelle (24 November 2016). "Holding-on: co-evolution between infant carrying and grasping behaviour in strepsirrhines". Scientific Reports. 6 (37729): 37729. Bibcode:2016NatSR...637729P. doi:10.1038/srep37729. PMC 5121892. PMID 27883046.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Simulated Evolution Gets Complex. Trnmag.com (8 May 2003). Retrieved on 2011-12-06.
- ^ Adami, C.; Ofria, C.; Collier, T. C. (2000). "Evolution of biological complexity". PNAS. 97 (9): 4463–8. arXiv:physics/0005074. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.4463A. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.9.4463. PMC 18257. PMID 10781045.
- ^ Earl, D. J.; Deem, M. W. (2004). "Evolvability is a selectable trait". PNAS. 101 (32): 11531–6. arXiv:q-bio/0407012. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10111531E. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404656101. PMC 511006. PMID 15289608.
- ^ a b Stemmer, W.P. (1994). "DNA shuffling by random fragmentation and reassembly: in vitro recombination for molecular evolution". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91 (22): 10747–51. Bibcode:1994PNAS...9110747S. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.22.10747. PMC 45099. PMID 7938023.
- ^ Sauter, E. (27 March 2006). ""Accelerated Evolution" Converts RNA Enzyme to DNA Enzyme In Vitro". TSRI – News & Views. 6 (11).
- ^ Molecular evolution. kaist.ac.kr
- ^ In Vitro Molecular Evolution. Isgec.org (4 August 1975). Retrieved on 2011-12-06.
- ^ Oswald, Tom (18 July 2001). "Digital organisms used to confirm evolutionary process". EurekAlert! Science News. American Association for the Advancement of Science.
- ^ Dybas, Cheryl (7 May 2003). "Artificial life experiments show how complex functions can evolve". EurekAlert! Science News. American Association for the Advancement of Science.
- ^ Clune, J; Goldsby, H. J.; Ofria, C.; Pennock, R. T. (2011). "Selective pressures for accurate altruism targeting: Evidence from digital evolution for difficult-to-test aspects of inclusive fitness theory" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society. 278. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2011.
Sources[edit]
- Biological science. Oxford. 2002.
- Clegg, C.J. (1998). Genetics & evolution. London: J. Murray. ISBN 978-0-7195-7552-5.
- Coyne, Jerry A. (2009). Why Evolution is True. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-923084-6.
- Darwin, Charles 24 November 1859. On the Origin of Species by means of Natural Selection or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. London: John Murray, Albemarle Street. 502 pages. Reprinted: Gramercy (22 May 1995). ISBN 0-517-12320-7
- Dawkins, Richard (2009). The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution. Bantam Press. ISBN 978-1-4165-9478-9.
- Endler, John A. (1986). Natural selection in the wild. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-08387-2.
- Fitzhugh, Kirk (2006). "-1-'Evidence' For Evolution Versus 'Evidence' For Intelligent Design: Parallel Confusions". Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
- Grant, Peter R.; Grant, B. Rosemary (2014). 40 Years of Evolution: Darwin's Finches on Daphne Major Island. Princeton University Press. p. 432. ISBN 978-0691160467.
- Hill, A.; Behrensmeyer, A. K. (1980). Fossils in the making: vertebrate taphonomy and paleoecology. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-04169-8.
- Kluge, Arnold G. (1999). "The Science of Phylogenetic Systematics: Explanation, Prediction and Test". Cladistics. 15 (4): 429–436. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.1999.tb00279.x. hdl:2027.42/73926. PMID 34902942. S2CID 6034651.
- Laurin, Michel (2000). "Early tetrapod evolution" (PDF). Tree. 15 (3): 118–123. doi:10.1016/s0169-5347(99)01780-2. PMID 10675932. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 10 November 2017.
- Mayr, Ernst (2001). What evolution is. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-04426-9.
- Paul, C.R.C.; Donovan, S.K. (1998). The adequacy of the fossil record. New York: John Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-96988-4.
- Prothero, Donald (2007). Evolution: What the Fossils Say and Why it Matters. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0231139625.
- Shubin, Neil (2008). Your Inner Fish:A Journey Into the 3.5 Billion-Year History of the Human Body. Random House. ISBN 978-0-375-42447-2.
- Sober, Elliott (2008). Evidence and Evolution: The logic behind the science. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87188-4.
External links[edit]
- National Academies Evolution Resources
- TalkOrigins Archive – 29+ Evidences for Macroevolution: The Scientific Case for Common Descent
- TalkOrigins Archive – Transitional Vertebrate Fossils FAQ
- Understanding Evolution: Your one-stop source for information on evolution
- National Academy Press: Teaching About Evolution and the Nature of Science Archived 2 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Evolution — Provided by PBS.
- Evolution News from Genome News Network (GNN)
- Evolution by Natural Selection — An introduction to the logic of the theory of evolution by natural selection
- Howstuffworks.com — How Evolution Works
- 15 Evolutionary Gems